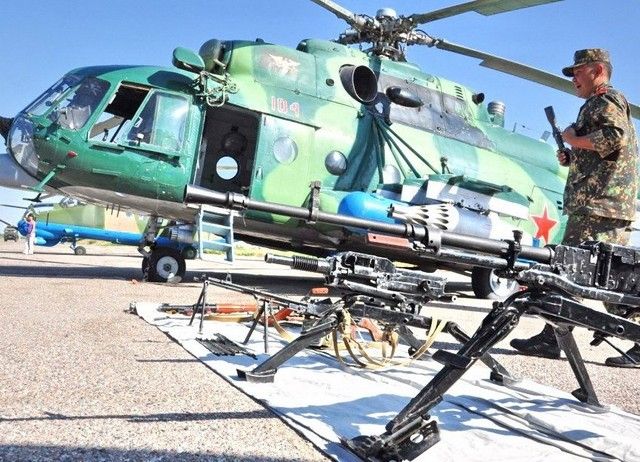
Kazakhstan’s returnees frustrated by cold shoulders
ALMATY (TCA) — Despite the official welcome policy of Kazakhstan’s authorities, ethnic Kazakhs that have returned to their historical homeland from neighboring countries experience hardships and often face unwelcome attitudes from the local population. We are republishing this article on the issue, written by Almaz Kumenov, originally published by Eurasianet:
The joy that Tursynzhan Yesenalyuly felt in moving to his ethnic homeland of Kazakhstan from China four years ago wore off pretty quickly.
Yesenalyuly, 44, lives with his three-year-old daughter in a cramped rented house in the village of Teskensu, around 80 kilometers east of Almaty, the business capital.
“I have no property, no job and no support. I need food and clothing for my child. This wasn’t what I dreamed about when I returned to the land of my forefathers. And this is decidedly not what Kazakhstan’s authorities promised us,” Yesenalyuly told Eurasianet.
In the immediate wake of independence, Kazakhstan emulated the experience of countries like Israel by flinging its doors open to ethnic kinfolk dispersed around the surrounding region. Ever since, however, the arriving migrants – known as Oralman, from the Kazakh word for returnees – have faced a battle for acceptance and have often struggled to prosper. But their complaints about lack of support from the government get short shrift from many who feel Oralmans have been given too many handouts.
The bulk of ethnic Kazakh communities abroad are the descendants of people who fled their native land around the start of the Soviet experiment, when political unrest, repression, forced collectivization and famine prevailed. The main destinations were China, other republics of Central Asia and Mongolia.
When the right-of-return program was enacted in the early 1990s, there were several urgent goals in mind.
Anuar Galiyev, a history professor at Al-Farabi Kazakh National University, explained that the dissolution of the Soviet Union sparked a mass flight of ethnic Russians, leading to a demographic collapse. New people were desperately needed to make up the numbers.
Another core, if often unspoken, notion was that the proportion of ethnic Kazakhs as a percentage of the broader population should increase. Under the last census to be carried out in Soviet times, ethnic Kazakhs accounted for less than 40 percent of the total population of what was then the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic.
According to official figures, more than 1 million have to date seized the opportunity to resettle in Kazakhstan, mainly coming from China and Uzbekistan.
The thought in the early 1990s was that arriving migrants could be resettled in sparsely populated rural locations and be put to work in underdeveloped sectors of the economy. Another history professor, Gulnara Mendikulova, told Eurasianet that the demand was mainly for people able to work on the land and raise livestock.
Yesenalyuly indeed had a background in agriculture, although since moving to Kazakhstan he has made his paltry income mainly from working on building sites and he has been unable to find a permanent position. One major problem is that he is unable to speak Russian, which often remains a requirement to find good work in urban areas. Yesenalyuly told Eurasianet he has had to borrow money to survive and is now drowned in debt, adding that he doesn’t know who to turn to for help.
“Why isn’t there an organization to help out Oralmans?” he asked.
Serikzhan Bilash, an Oralman rights activist who moved to Kazakhstan from China two decades ago, echoed those sentiments in an interview with Eurasianet.
“The World Association of Kazakhs, which was created by the authorities, has been called on to support the Oralmans. But this organization is so passive that people do not even know about its existence,” Bilash said.
The issue of assistance is a contentious one though.
From the outset, the government ostensibly put many theoretical sweeteners on the table for the new arrivals, from subsidized relocation and free accommodation to jobs, land and some benefit payments. But many complain much of this support is not quite as helpful as it first appears. Homes specially built for Oralmans are often in remote locations, which complicates finding decent work and integrating with the wider population.
The authorities have expressed a preference for seeing Oralmans resettle in the northern regions of the country, but those areas often hold little appeal.
“The south is more appealing for migrants — their relatives live there, it is a warmer climate and they are among people speaking their own tongue. In the north, where the proportion of Kazakhs is lower, Russian dominates,” said Galiyev, the history professor at Al-Farabi.
In order to encourage migration, the government in Astana greatly simplified the naturalization procedure for those who could demonstrate ethnic and familial ties to Kazakhstan. Despite the eased procedures, however, bureaucracy is often slow. In April, President Nursultan Nazarbayev signed legislation extending the amount of time Oralmans can remain in Kazakhstan while they regularize their status. Previously it was only one year. Applicants can now apply for indefinite permission to remain while the procedure is completed.
And if the authorities were welcoming, local communities were not always so warm. The term Oralmanophobia has even been coined to describe resentment felt by many native-born residents of Kazakhstan.
“Oralmans are different, they are not like us,” Kuanysh Koishbayeva, a 43-year-old resident of Viktoriya village, in the Almaty region, told Eurasianet. “They have different values and attitudes. And at the same time, they try to teach us how to be proper Kazakhs. And they demand so much from the government. Who do they think they are?”
Duman Bykai, editor of Kazakh-language newspaper Kala men Dala (City and Steppe), said that much of the animosity comes from the Russian-speaking part of the population, some of which takes exception to what they perceive as overly nationalist rhetoric from repatriates. The terms “national-patriots,” natspaty for short, is often deployed with an undertone of contempt.
“We have a lot of these activists among the repatriates who came to Kazakhstan to become part of the nation’s rebirth,” said Bykai, who himself relocated from the Russian city of Tyumen.
Oralman activism is now taking a geopolitical turn.
In recent months, ethnic Kazakhs who moved from China have become increasingly exasperated at the fate of relatives and friends who stayed behind. Rights groups have sounded the alarm about the widely documented repression of the ethnic Kazakh, Uyghur and Kyrgyz minorities at the hands of Chinese authorities. An article by The Associated Press published last month detailed the harrowing account of an ethnic Kazakh man imprisoned in a Chinese indoctrination camp designed to intimidate internees into renouncing their Islamic faith.
Around 1.5 million ethnic Kazakhs live in China, according to official figures, and some in the Oralman community, like Bilash, complain that Astana is not lifting a finger to help them. Kazakhstan’s government has indeed been notably mute about charges of rights violations, a position that commentators argue is motivated by Astana’s unwillingness to spoil relations with a valuable economic partner.
In apparent acknowledgement of the creeping discontent, China’s ambassador to Kazakhstan, Zhang Hanhui, insisted at a press conference in November that any detentions that had occurred were intended to prevent the threat of separatism and terrorism in his country’s western Xinjiang province.
Yesenalyuly, the father of the three-year-old, said his wife is among those being prevented from leaving China and said she too had been held at a “reeducation center.” In spite of his hardships, this may be a reason he and those like him keep trying to make a go of life in Kazakhstan.
“My ancestors lived on this land. Finally, I feel that I am home, and that is the main thing,” he said.