Tokayev’s U.S. Visit Advances Kazakhstan’s Economic Agenda
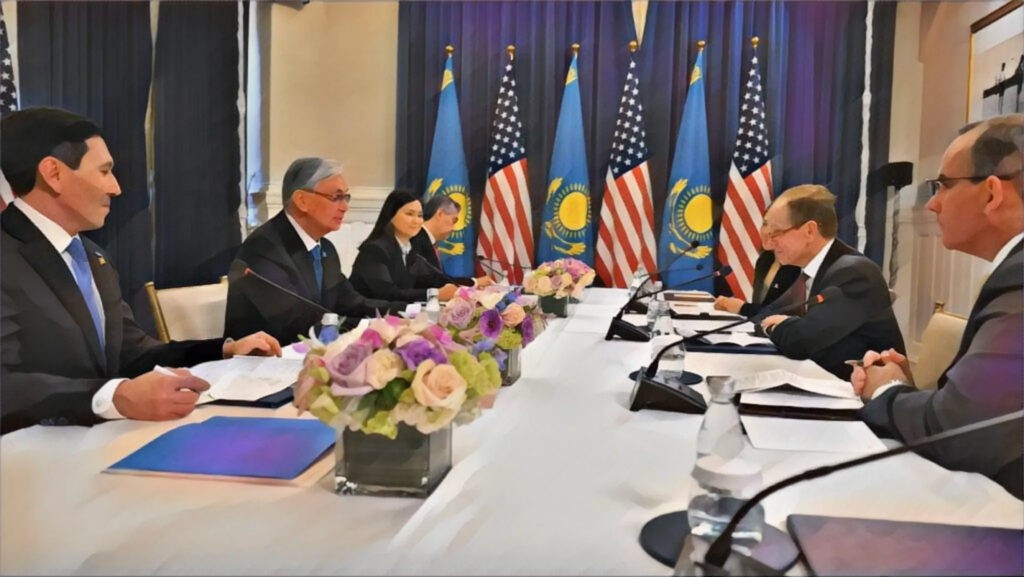
The visit of Kazakh President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev to the United States provided an opportunity for targeted negotiations with major international corporations and financial institutions, centered on long-term investment, production localization, and Kazakhstan’s integration into global value chains. One of the key outcomes was the signing of an investment agreement worth approximately $180 million between Kazakhstan’s Ministry of Agriculture and Mars, Incorporated. The company plans to build a pet food production plant in the city of Alatau. The project will focus on the deep processing of agricultural raw materials and the production of high-value-added goods. Mars CEO Poul Weihrauch noted that the Kazakhstan facility will serve as a base for expanding the company’s presence in Central Asia and neighboring regions. A separate round of negotiations focused on healthcare. During talks with Ashmore Group, discussions centered on a proposal to build an international clinic in partnership with Ashmore Healthcare International and Samruk-Kazyna Invest, with the involvement of the Mount Sinai Health System as the operator. The initiative aligns with Kazakhstan’s strategy to develop medical infrastructure and medical tourism, as well as the Open Investment Partnership program targeting high-tech sectors of the economy. Aviation was another major component of the visit. At a meeting with Boeing executives, Tokayev confirmed the interest of Kazakh carriers Air Astana, SCAT Airlines, and VietJet Qazaqstan in expanding cooperation. Air Astana expects to receive Boeing 787 Dreamliner aircraft in the second half of 2026, which could pave the way for the launch of direct flights between Kazakhstan and the U.S. SCAT, meanwhile, is considering both the acquisition of additional aircraft and the establishment of its first maintenance and repair center at Shymkent Airport in partnership with an American company. The visit concluded with negotiations involving the U.S. International Development Finance Corporation (DFC). Its CEO, Ben Black, said Washington views Kazakhstan as a key partner in Eurasia. The discussions focused on projects in the mining sector and the development of transport and transit infrastructure critical for regional and interregional trade. According to the World Investment Report 2025 (UNCTAD), Kazakhstan overwhelmingly dominates foreign direct investment (FDI) in Central Asia. In 2024, Kazakhstan’s inward FDI stock stood at about $151 billion, far exceeding Turkmenistan (about $45 billion), Uzbekistan (about $17 billion), and Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan (around $4 billion each). The negotiations in Washington point to Kazakhstan’s focus on building long-term institutional partnerships rather than pursuing isolated investment deals, a signal intended to reassure international investors about the stability and openness of the market. As previously reported by The Times of Central Asia, Tokayev also took part in the inaugural meeting of the Board of Peace in Washington, where Kazakhstan signaled its willingness to contribute to Gaza’s reconstruction and broader stabilization efforts, including potential financial support and participation in peacekeeping initiatives.