EDB Forecasts Strong Economic Growth in 2026 for Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
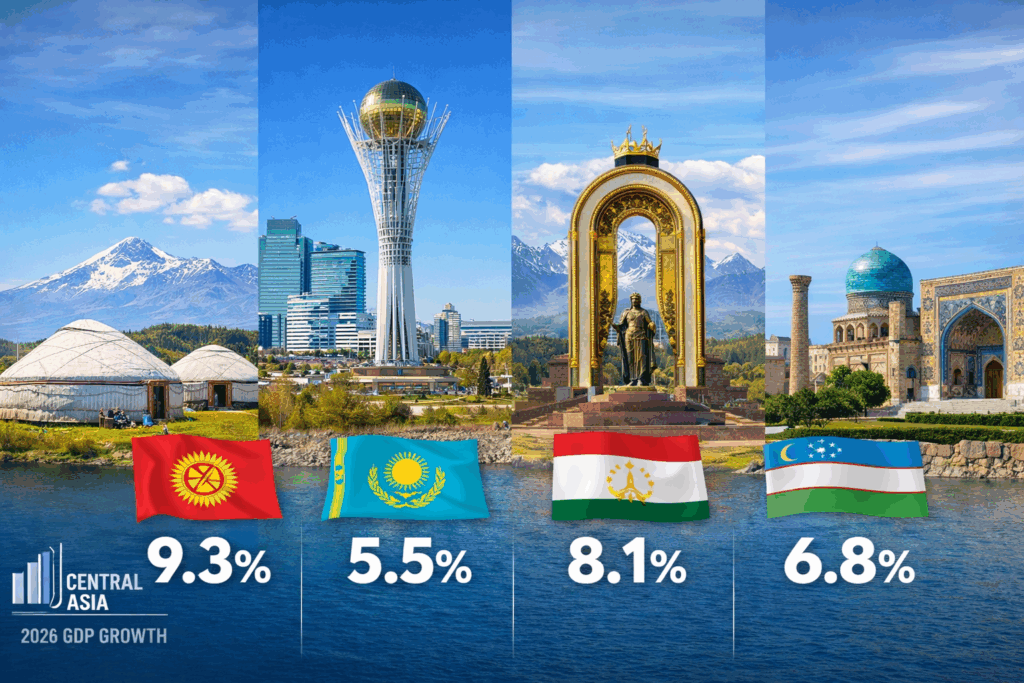
On December 18, the Eurasian Development Bank (EDB) published its Macroeconomic Outlook for 2026-2028, reviewing recent economic developments and offering projections for its seven member states: Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. According to the report, aggregate GDP growth across the EDB region is forecast to reach 2.3% in 2026. Kyrgyzstan (9.3%), Tajikistan (8.1%), Uzbekistan (6.8%), and Kazakhstan (5.5%) are expected to remain the region’s fastest-growing economies. After two years of rapid expansion, the region’s GDP growth is set to moderate to 1.9% in 2025, down from 4.5% in 2024, mainly due to a slowdown in Russia’s economy. Although lower oil prices are expected to reduce export revenues for energy exporters such as Kazakhstan and Russia, the impact on overall growth will be limited. Meanwhile, net oil importers, including Armenia, Belarus, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan, will benefit from improved terms of trade and reduced inflationary pressure. High global gold prices will support foreign exchange earnings for key regional exporters, including Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. The report also notes a gradual decline in the U.S. dollar’s share in central bank reserves across the region, though its role in international settlements remains stable. Kazakhstan Kazakhstan’s economy is projected to grow by 5.5% in 2026, supported by the implementation of the National Infrastructure Plan and the state program “Order for Investment,” which are expected to cushion the effects of lower oil prices. Growth in non-commodity exports will also play a stabilizing role. Inflation is forecast to decline to 9.7% by the end of 2026, after peaking early in the year due to a value-added tax (VAT) increase. The average tenge exchange rate is expected to be KZT 535 per U.S. dollar, underpinned by a high base interest rate and rising export revenues. Kyrgyzstan Kyrgyzstan is forecast to lead the region in GDP growth at 9.3% in 2026, driven by higher investment in transport, energy, water infrastructure, and housing construction. Inflation is expected to ease to 8.3%, although further declines will be constrained by higher tariffs and excise taxes. The average exchange rate is projected at KGS 89.2 per U.S. dollar, supported by robust remittance inflows and high global gold prices, gold being the country’s main export commodity. Tajikistan Tajikistan is projected to maintain high GDP growth of 8.1% in 2026, fueled by capacity expansion in the energy and manufacturing sectors, along with rising prices for gold and non-ferrous metals. Inflation is expected to reach 4.5% by year-end. The somoni is expected to remain stable, with an average exchange rate of TJS 9.8 per U.S. dollar, supported by growth in exports and remittances. Uzbekistan Uzbekistan’s economy is forecast to expand by 6.8% in 2026, sustained by strong investment activity and favorable gold prices. Inflation is projected to decline to 6.7%, helped by tight monetary policy and a stable exchange rate. The average soum exchange rate is expected to be UZS 12,800 per U.S. dollar, supported by high remittances and increased metal exports.