Viewing results 1 - 6 of 2
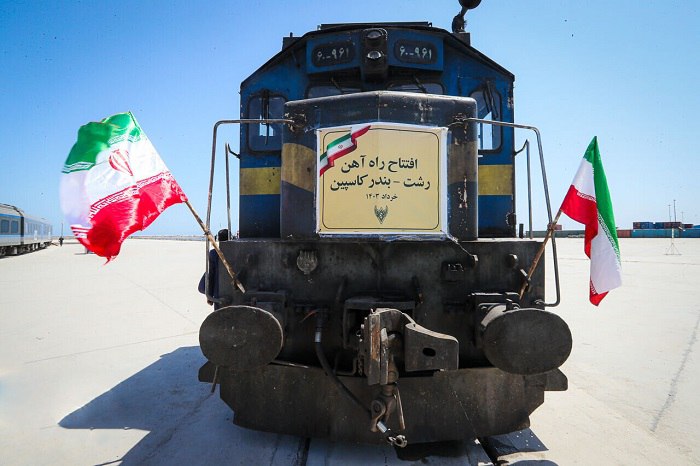
Turkmenistan will start the transit of cargo along the Resht-Kaspian railroad line in Iran, as reported by the publication, Turkmenistan: Golden Age, citing Milad Salehi, the Director General of Railways of the Islamic Republic of Iran. Sulfur transit from Turkmenistan will start along this route next week. The Resht-Kaspian railroad is an important part of the North-South international transportation corridor connecting the Caspian Sea with the Persian Gulf and the Sea of Oman. It also links the north and south of the country. This route opens up new opportunities for cargo transit from Central Asia to the Middle East and South Asia.
A roundtable discussion on Central Asia’s cooperation with the European Union was held on February 2nd at the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Office in Brussels, Belgium. The event brought together representatives from UNDP, the European Commission, and ambassadors of Central Asian countries to the EU. The participants discussed ways to boost sustainable economic growth in the region by creating partnerships to ensure a steady supply of critical raw materials, and enhancing the efficiency of the Trans-Caspian Corridor, also known as the Middle Corridor. The participants also emphasized the importance of supporting the transition of Central Asian economies towards environmentally friendly and sustainable systems, in line with their climate commitments on emissions. Katarzyna Wawiernia, the UNDP resident representative in Kazakhstan, emphasized the significance of the Trans-Caspian Corridor and the sustainable development of the Caspian region overall. “We recommend adopting a sustainable landscape management approach for the future development of the Caspian region. In this regard, UNDP, in partnership with the Government of Kazakhstan, is planning a large-scale initiative to promote an integrated ecosystem-based approach to conserve key species and habitats of the Caspian Sea and ensure sustainable economic development for local communities. Throughout its history, the Caspian Sea has been a significant source of biological resources. They make up a single ecosystem that requires strong protection from natural and people-made factors,” Ms Wawiernia said.