Can Special Economic Zones Become a Driver of Economic Growth in Kazakhstan?
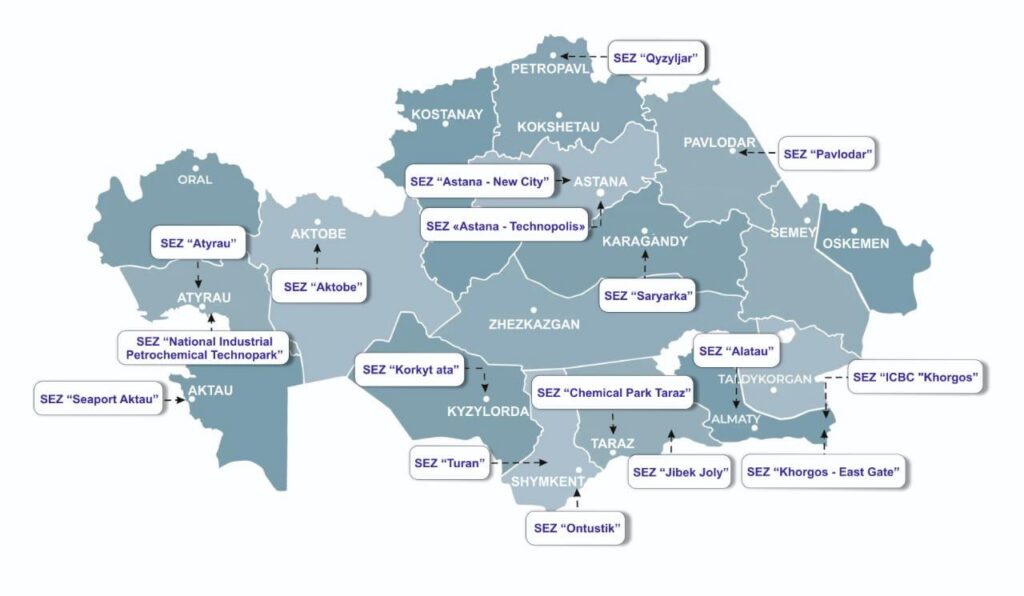
Kazakhstan currently has 17 special economic zones (SEZs) operating across 14 regions, three of which were created in 2025. How effective is this tool for attracting investment, reducing import dependence, and developing exports? And how will the SEZ model evolve within the framework of the Single Coordination Center? Yerlan Kusainov, Deputy Chairman of the Board of JSC Kazakhstan Center for Industry and Export “QazIndustry,” discussed these issues with The Times of Central Asia. TCA: Kazakhstan currently has 17 SEZs. How many companies operate in them, and what is the total volume of production? Kusainov: There are 1,144 participants registered in SEZ territories. Of these, 558 projects are already operational, while another 586 are in the implementation stage. Since the establishment of the zones, enterprises have produced goods worth 13.9 trillion tenge (about $28 billion). The current occupancy rate of the SEZs is 42.4%. This indicator is dynamic and may change as new contracts are signed or as some participants cease operations. TCA: What types of products are manufactured in the SEZs, and how does this contribute to reducing import dependence? Kusainov: The SEZs cover a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, construction, transport and logistics, and tourism. For example, the Aktau Seaport SEZ is implementing projects in the chemical industry, including the production of caustic soda and hydrochloric acid by Topan Chemical Industries. These products are widely used in metallurgy, the oil and gas industry, and water treatment. Previously, a significant portion of such products was imported, but production is now being localized in Kazakhstan. A major petrochemical cluster is being formed in the Jibek Joly SEZ. Projects there include the production of mineral fertilizers, chemical reagents, and polymer products. Participating companies include HIM-plus, KPM Plast, Chemical Engineering, and C9 Technologies. These projects are expected to supply the domestic market while also supporting exports. In the Pavlodar SEZ, projects are being implemented in metallurgy and petrochemicals. These include the production of calcined petroleum coke by UPNC-PV, car wheels by Vector Pavlodar, and aluminum ingots and alloys by LeichtMetall KZ and Unimetals. These products are exported to markets in Europe and Asia. The Ontustik SEZ focuses on the textile industry, where a full cotton-processing cycle has been established, from raw materials to finished products. Enterprises there produce cotton and synthetic yarn, carpets, and other textile goods. Another important site is the Park of Innovative Technologies SEZ, where projects in digital technologies and electronics are being developed. Key participants include the Institute of Physics and Technology, KT Cloud Lab, which is building a data center, and DS Multimedia CA, which manufactures electronic components. Together, these projects contribute to reducing import dependence and building export-oriented industries. TCA: What is the export volume of SEZ enterprises? Kusainov: The total export volume from SEZ enterprises has reached about $2 billion. In 2025 alone, exports amounted to approximately $490 million, compared with $148 million in 2021, an increase of 231%. TCA: How much investment has been attracted through the SEZs? Kusainov: Over the entire period of...