From Test Sites to Power Plants: Kazakhstan’s Journey Towards a Nuclear Referendum
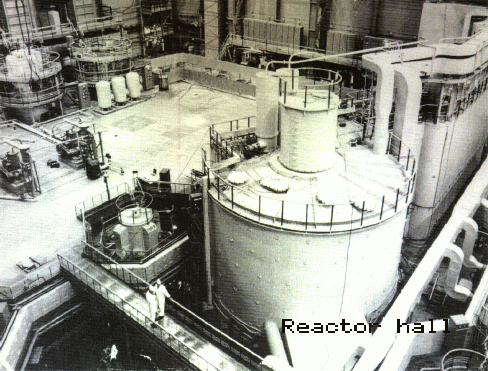
The history of nuclear power in Kazakhstan has many chapters: the arms race, the suffering of people due to test sites, the highest achievements in the name of science, and the service of the nuclear industry for the benefit of society are closely intertwined here. On the eve of the referendum on Kazakhstan's first atomic power plant, it is necessary to revisit these pages in history. A dark past Construction of the Semipalatinsk nuclear test site began in the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic in 1947. The test site is located on the border of the Semipalatinsk (now Abay), Pavlodar, and Karaganda regions, 130 kilometers northwest of Semipalatinsk (now Semey), on the left bank of the Irtysh River. On its territory is the previously closed city of Kurchatov, renamed as such in honor of Soviet-era physicist, Igor Kurchatov. The first nuclear weapons test held in the Soviet Union was conducted at this site on August 29, 1949. The power of the bomb totaled 22 kilotons. From 1949 to 1989, at least 468 nuclear tests were conducted at the Semipalatinsk nuclear test site. The long-term operation of this site and its negative impact on residents' health and the surrounding environment help to explain the fear of nuclear energy in Kazakhstan. Two million people were affected across 300 square kilometers; with all agriculture banned, a vast swathe of land still remains off-limits. Pregnancies are still screened for possible termination, with 6% of babies born “polygon” (the name for the "closed zone".) [caption id="attachment_23475" align="aligncenter" width="1200"] Polygon baby, National Museum of Kazakhstan, Astana; image: TCA, Stephen M. Bland[/caption] Shutdowns and shortages On August 29, 1991, Kazakhstan's first president, Nursultan Nazarbayev, closed the Semipalatinsk test site. Prior to this, citizens had held rallies protesting against nuclear testing and its development. By 1994, Kazakhstan had voluntarily relinquished its part of the USSR's nuclear arsenal. On May 15, 1992, the National Nuclear Center in the city of Kurchatov was established based on the complex of the former Semipalatinsk test site. The Center deals with eliminating the consequences of nuclear tests and also conducts active and multidisciplinary scientific activities on the remaining research reactors in Kurchatov. Scientific research occurs internationally and touches upon safety technologies, the space program, and more. In 1957, the Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Kazakh SSR Academy of Sciences was founded near Almaty (then Alma-Ata), where the VVR-K reactor, which is still operating today, was launched in 1967. The reactor was shut down in the late 1980s after the Chernobyl disaster and the earthquake in Spitak (Armenia); it was restarted in 1997, and the complex underwent safety and seismic reinforcement modernization. The Institute owns eight experimental facilities: the VVR-K research reactor, a "Критический стенд" lit. "critical stand," and six charged particle gas pedal complexes. In 1972, a unique fast neutron reactor BN-350 was launched in Aktau (then Shevchenko) at the Mangistau Atomic Energy Combine (MAEC). The reactor provided the Mangistau Peninsula with electricity and heat, and supported the operation of desalination plants...
4 months ago