Robust Economic Growth in EDB Member States
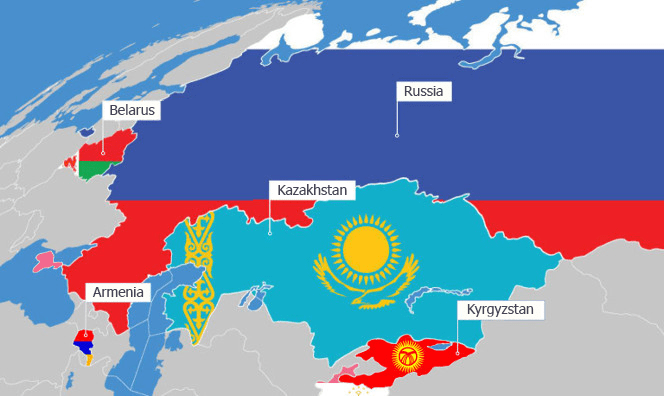
The latest Macroeconomic Review for the EDB’s six member states — Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Tajikistan – was released by the Eurasian Development Bank on April 12th. Despite the challenging external economic environment, the report illustrates robust economic growth amongst all its members in January-February this year and according to short-term economic activity indicators, high GDP growth is set to continue. Fuelled by capital investment, Kazakhstan’s economy expanded by 4.2%, and Kyrgyzstan experienced a GDP surge of 8.6%, largely due to intensified investment activity, which spiked to 55%. Propelled by a dynamic increase in industrial output, economic activity in Armenia rose by 13.6%, and Belarus’s economy grew by 4% during the same period, boosted by manufacturing and retailing industries. In Russia, industrial production remains the prime driver of economic growth, raising the nation’s GDP by 6.0%, and Tajikistan’s high growth rates are maintained by consumption and investment sectors. In conclusion, the EDB reports that domestic demand within its represented countries is propelled by national projects, including increased public investment in Armenia, import substitution programs in Belarus and Russia, and the development of mechanical engineering in Kazakhstan and energy sectors in Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan.