Kyrgyzstan Combats Pastureland Degradation to Safeguard Livestock Farming
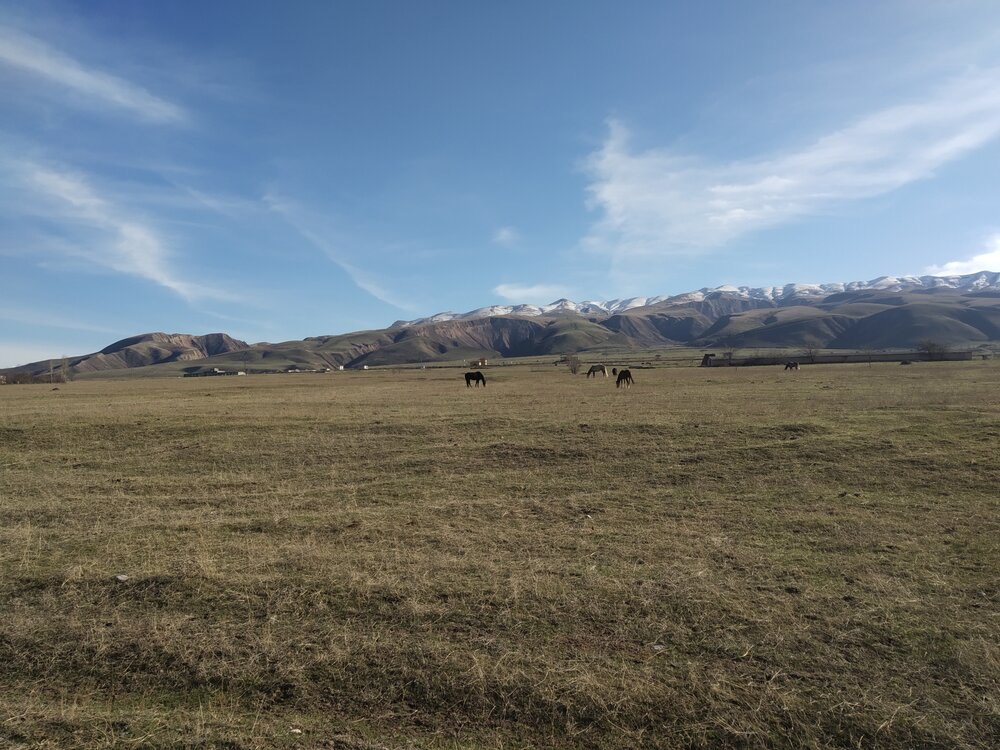
Pastureland is a strategic asset for Kyrgyzstan, where agriculture forms the backbone of rural livelihoods. A majority of the population depends on raising sheep, cattle, and horses for food and income. However, widespread degradation of pastureland, especially near settlements, now poses a growing threat to the country's livestock sector. Farmers and herders increasingly favor grazing their animals on easily accessible village pastures, leaving more remote areas underused. This uneven distribution has led to overgrazing and deterioration of pastures near populated areas. According to the Ministry of Water Resources, Agriculture and Processing Industry, more than 139,000 hectares of village pastures have been degraded and require restoration. Policy Response: Grazing Restrictions and Seasonal Rotation In response, the ministry has issued a directive mandating seasonal rotation of grazing lands. Under the new policy, farmers must move their livestock to distant pastures between April 15 and September 15 each year. This initiative aims to: Preserve natural ecosystems Promote responsible use of state-owned pastureland Enhance livestock productivity through improved pasture management Grass Reseeding Campaign Underway To rehabilitate affected areas, the government has launched a nationwide reseeding campaign. For the 2025 season, the Ministry of Agriculture has procured 94,462 kilograms of sainfoin seeds and 137,725 kilograms of other pasture grass seeds. These have been distributed across regions for use by local farmers and pasture users. The reseeding effort is expected to help restore 15,299 hectares of degraded pastureland. As of now, 2,810 hectares have already been sown with a mix of sainfoin and pasture grasses. This proactive approach underscores Kyrgyzstan's commitment to sustainable agriculture and long-term food security. Ensuring the health of its pastures is not just an environmental necessity, it’s an economic imperative for the thousands of families who depend on livestock farming for their livelihoods.