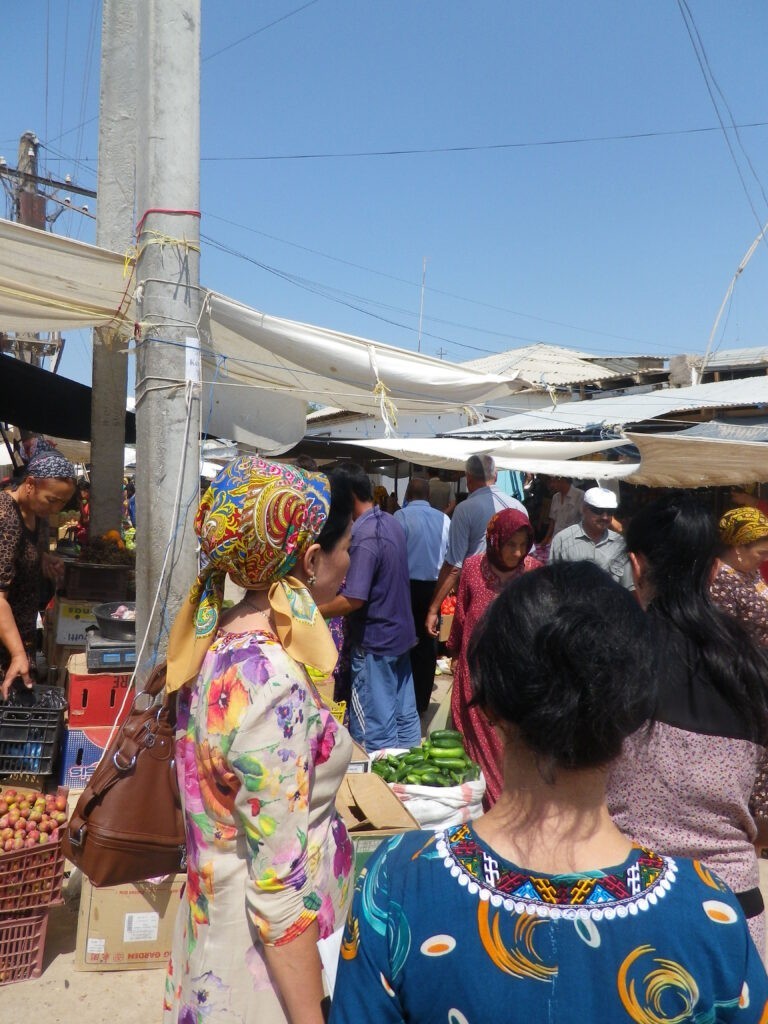
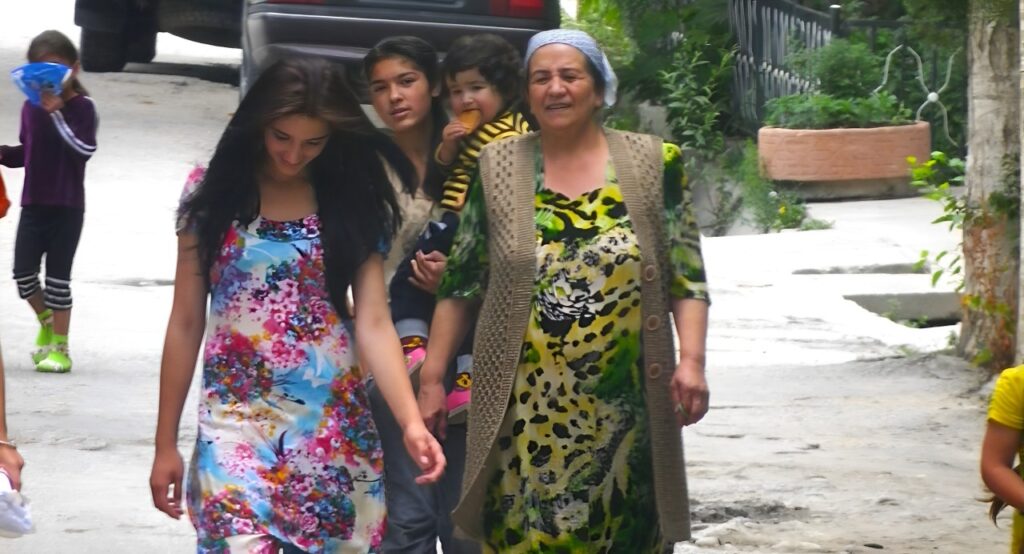Residents of Tajikistan will face fines ranging from 8,000 to 65,000 somoni for "importing and selling clothes that do not correspond to the national culture" and for wearing such clothes in public places, as reported by Radio Ozodi. These regulations are outlined in Article 18 of the new version of the law "On Regulation of Traditions and Rites" and the Code of Administrative Offenses. The drafts were adopted by parliamentarians on May 8 this year. "In the draft law 'On the Regulation of Traditions and Rites,' a corresponding prohibiting norm is included in part two of Article 18. For its violation, amendments and additions to Article 481 of the Code of Administrative Offenses provide for administrative responsibility," explained Mavludakhon Mirzozoda, a deputy of the lower house of Tajikistan's parliament. Article 481 of the current Code of Administrative Offenses addresses not only Article 18, but also broader non-compliance with the norms of the Law on the Regulation of Traditions and Rites. According to this article: Individuals will be fined 7,920 somoni ($733). Officials will be fined 39,600 somoni ($3,665). Legal entities will be fined 57,600 somoni ($5,333). Individual entrepreneurs, scientists, and religious figures will be fined 54,000 somoni ($4,998). For repeated violations, fines will range from 46,000 to 86,000 somoni. The recent amendments have updated this article, although changes to the fine amounts are yet to be confirmed. The average wage in Tajikistan is approximately $172 a month. According to the current legislation, the amendments to the law come into force upon publication in the official press after approval by the Majlisi Milli (lower house) and the president's signature. However, citizens are already being compelled to comply with these new regulations. The current law does not specify which clothing is considered alien to Tajik national culture. Experts suggest that the law likely pertains to women's national dress, although the text itself does not differentiate between men's and women's clothing. Reactions within Tajik society have been mixed. Some residents of Dushanbe, during a street survey, expressed their opinion that people should have the freedom to choose their own attire without compulsion. Tajik authorities have long campaigned to encourage the wearing of national dress and to discourage the adoption of foreign styles. They prohibit women from wearing black clothing, black headscarves, and hijabs, considering them alien to Tajik culture and traditions. Although mini-skirts, sweaters, dresses with cleavage, tops, and transparent fabrics were also banned at one point, these restrictions were quickly "forgotten."