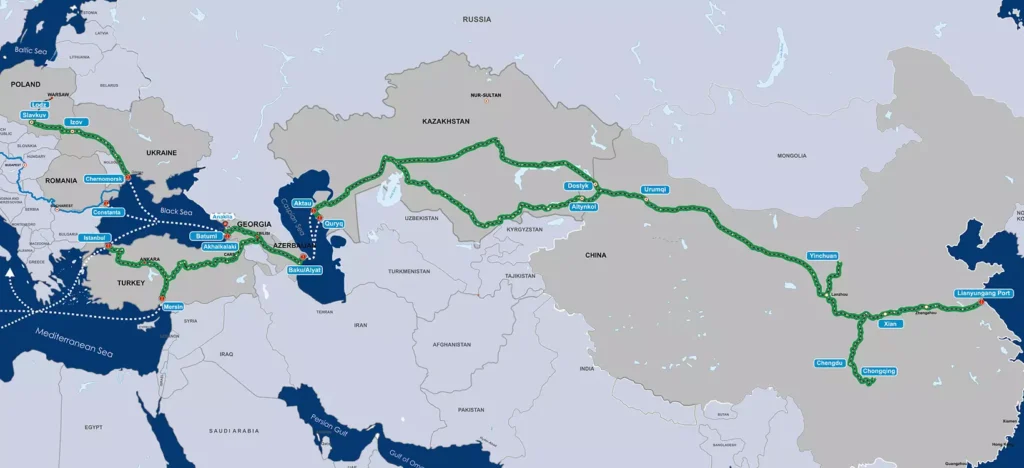
In light of the current geopolitical situation in the world, many countries are puzzled by the search for new alternative transport routes. One of these is the Trans-Caspian International Transport Route (TITR), which runs through China, Kazakhstan, the Caspian Sea, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and further to Turkey and European countries. New transport corridors through which goods and raw materials can be exported by all modes of transport are a vital task for many countries, today. Such routes must first of all be safe, beneficial to all partners, and economically feasible. The TITR, or the “Middle Corridor”, as it is also called, falls into these criteria. It was conceived more than ten years ago and began operating in 2017. In recent years, this route has been experiencing a new round of development, and this is not surprising since it connects East and West whilst bypassing Russia. Today, this is a flagship cooperation project for many states. This transport artery, connecting China, Central Asia and Europe, can become a continental bridge of the Belt and Road, halving the time of cargo transportation and significantly reducing transport costs. The route encompasses 11,000 km of rail, and includes ten seaports. It originates in China at the port of Lianyungang, passing through Xi'an to Urumqi, through Kazakhstan - from the dry ports of Khorgos and Dostyk - to the ports of Aktau and Kuryk, the Azerbaijan (port of Alyat), Georgia (Tbilisi), and then through the Black Sea it continues onto Europe. It is noteworthy that this route is multimodal, that is, rail, sea and road transport can be used. The current capacity of the Trans-Caspian international transport route is 6 million tons per year. By 2025, it is planned to reach a level of 10 million tons per year. So, the potential is great. Assessing all possibilities, interested states intend to invest financial resources in the further development of this corridor and the expansion of its port and railway infrastructure, which will have a positive impact on the quality of services provided and reduce transportation times. Each side – China, Turkey, Azerbaijan and Kazakhstan – has its own benefit, and these countries have something to offer each other in much larger volumes than the current supplies. China intends to develop its western provinces, providing them with access to regional markets. Azerbaijan sees an opportunity to strengthen its transit role and become the largest transport hub. Türkiye, in turn, continues to extend its influence in Azerbaijan and Central Asia. As for Kazakhstan, there are fears that attacks by the Ukrainian Army on Russian oil refineries could lead to a blockage of the Caspian Pipeline Consortium (CPC), which supplies Kazakh oil to international markets. In this regard, a huge amount of work is being done to diversify, and the Trans-Caspian International Transport Route comes in handy here. The Kazakh company, KazMunaiGas has already purchased tankers, and there are agreements with Azerbaijan on access to the Baku-Supsa and Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan pipelines, through which Kazakhstan can transport about 2 million tons...