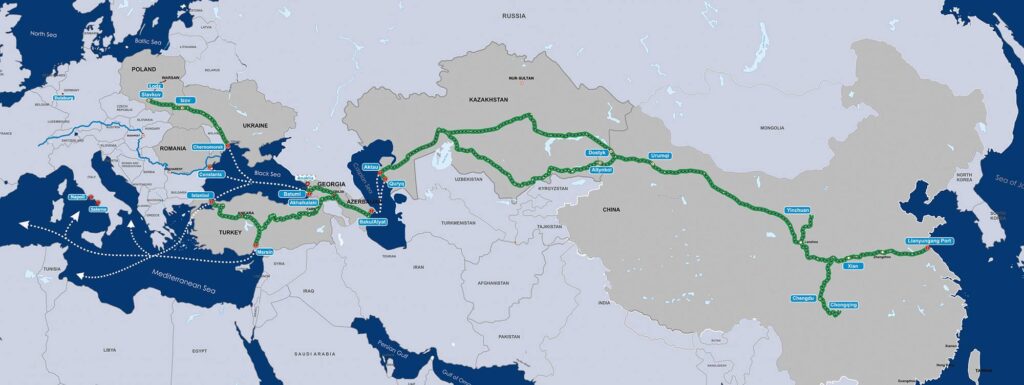
By Robert M. Cutler According to Samuel Doveri Vesterbye, director of the independent think-tank, European Neighbourhood Council (ENC), a small group of high-ranking cabinet officials, ambassadors and other diplomats met in a closed-door round-table on May 15, representing the EU, Türkiye and countries in the South Caucasus and Central Asia. The meeting, organized by Turkish organizations International Transporters Association (UND) and the Turkish Industry and Business Association (TUSIAD), focused on the synergy between the EU's Global Gateway initiative and the projects of the Trans-Caspian International Trade Route (TITR). The fact of the meeting taking place has been confirmed by Türkiye’s Permanent Delegate to the EU. Doveri Vesterbye writes that the meeting "consisted of less than 30 individuals mostly linked to diplomacy, transport, logistics, business, critical infrastructure security, policy-making and supply chains" and "brought together four different Directorate Generals (DGs) and more than 10 nationalities of Director-and-Ambassador level." Significantly, also according to Doveri Vesterbye, the development of high-level coordination committees is under way. The meeting’s assessment that the TITR is being funded faster than expected is an extremely positive development. Dr. S. Frederick Starr, a well-known American expert and a Distinguished Fellow for Eurasia at the American Foreign Policy Council, told The Times of Central Asia that "the activation and coordination of both European and Turkish institutions is essential not only for the financing and construction of this mega-project, but also for its successful management thereafter." This is a very stabilizing development for international commerce. As other corridors are increasingly volatile, it would help to insulate trade between China and Europe from supply-chain shocks. It will also benefit the participating states themselves. Starr explained that the continuing European and Turkish involvement in building out the TITR "will help the transit states of Central Asia and the [South] Caucasus to balance their relations with China and Europe and will thereby undergird their sovereignties. Such balance creates what is literally a 'win-win-win' situation." According to a mid-2023 report, prepared jointly by the EBRD and the EU Commission, an estimated €18.5 billion is required in infrastructure investments in order to improve Central Asia's transport connectivity. Potential growth in transit container traffic by 2040 could be over 40-fold, with significant spill-over effects on education, tech hubs, business and middle-class development. At the same time, the TITR has been reconceptualized as a driver of regional trade and economic growth along the entire Europe–Türkiye–South Caucasus–Central Asia trajectory, with special attention given to the latter two regions. The EU Commission and the EBRD have already funded €10.5 billion in Central Asia via loans and grant investments promised only a few months ago, in January this year, at the Global Gateway Investment Forum in Brussels. This pace suggests significant commitment by such large bureaucratic organizations, and it augurs well for the unlocking of funds from the European Investment Bank (EIB) for investment in Turkey. Doveri Vesterbye writes that the heads of EU member-state missions in Brussels (COREPER) will work to synchronize EIB investments, with special attention on reforming...