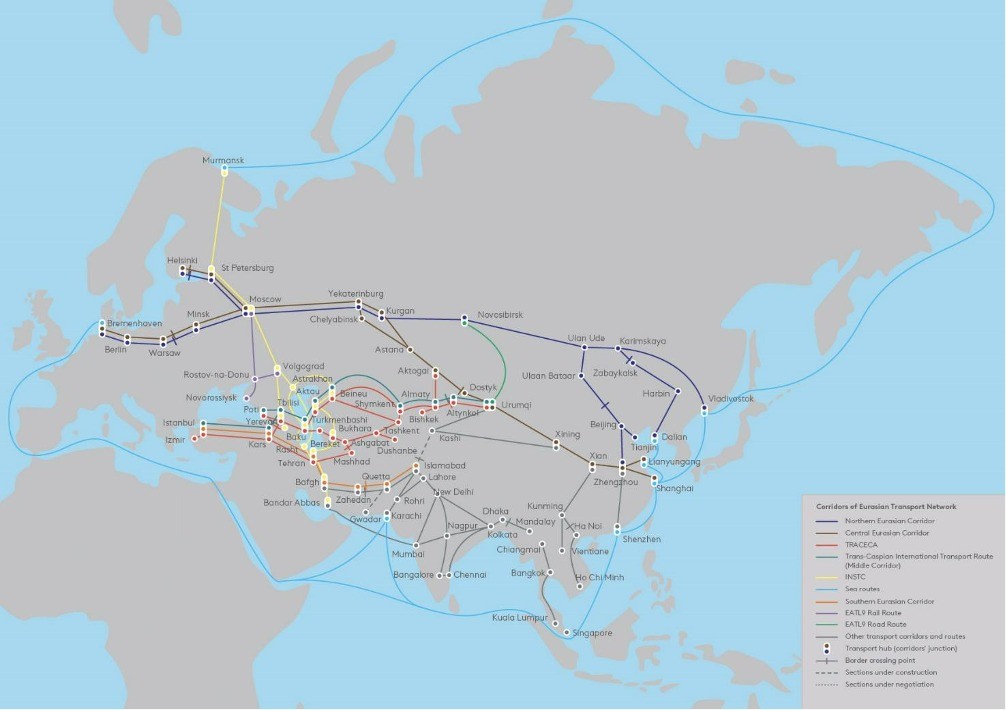
On 27 June, the Eurasian Development Bank (EDB) released a report titled “The Eurasian Transport Network”. The report introduces a new conceptual approach to future developments within the Eurasian Transport Network and outlines key projects and initiatives aimed at improving transport connectivity in Eurasia. The Eurasian Transport Network is a system of interconnected latitudinal and longitudinal international transport corridors and routes, facilitating intra- and trans-continental connectivity for Eurasian countries. It builds upon over 50,000 km of international east-west and north-south transport corridors, linking Asia, Europe, and the Middle East. The Eurasian Transport Network consists of five key international transport corridors: the Northern, Central and Southern Eurasian Corridors, TRACECA, and the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), along with branch lines and regional routes. According to EDB analysts, in 2023, international freight traffic along these five corridors of the Eurasian Transport Network totaled 260 million tons, including 3.6 million 20-foot containers (TEU). Compared to 2013, the volume of international container traffic has more than tripled. The most dynamic growth has been driven by foreign trade and transit container transit with China. Since 2013, the number of container trains to and from China via the Eurasian Economic Union countries and Central Asia has increased by a factor of 200. The EDB introduced the concept of a Eurasian Transport Network in 2021, and this report presents its detailed framework. Three years ago, the EDB released a report titled “The International North–South Transport Corridor: Promoting Eurasia’s Intra- and Transcontinental Connectivity”, which estimated that connecting international transport corridors would yield a 40% increase in freight traffic. In 2024, this projection was fully confirmed by the dynamic development of the INSTC and its linkage to TRACECA. The advancement of the Eurasian Transport Network is paving the way for the establishment of a transport hub in Central Asia. The development of multimodal transport and transit corridors is the only viable solution for Central Asian countries due to the significant distances between trade partners. Establishing a transport hub will facilitate an increase in international traffic, including transit. The EDB projects that freight traffic along the three main corridors running through Central Asia will increase by 1.5 times to 95 million tons by 2030. Container traffic is expected to grow even more rapidly, by almost two-thirds, reaching 1.7 million TEU. Evgeny Vinokurov, EDB Chief Economist, underlines that “at present, transportation costs for landlocked countries are 1.4 times higher than for coastal states. Even during the time of the Silk Road, trade routes in Central Asia were predominantly latitudinal, in the east-west direction. Building new north-south transportation links is a historic opportunity for Central Asia. This is an opportunity to become the continent’s transport hub, unlock new production niches and improve conditions for foreign trade, especially with West and South Asia.” The EDB concludes that given the limited investment opportunities facing most developing countries in Eurasia, a key area of cooperation to develop transport links in Eurasia is boosting the number of projects attractive to international development banks and private investors. This includes projects implemented...