Kazakhstan to Construct Seven New Offshore Vessels
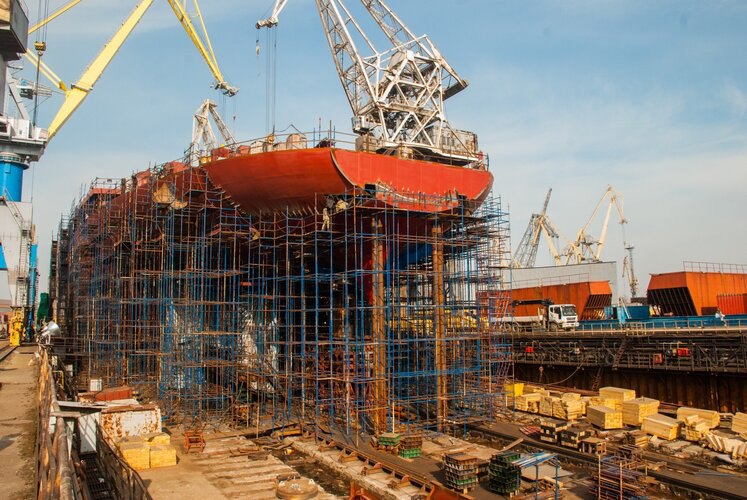
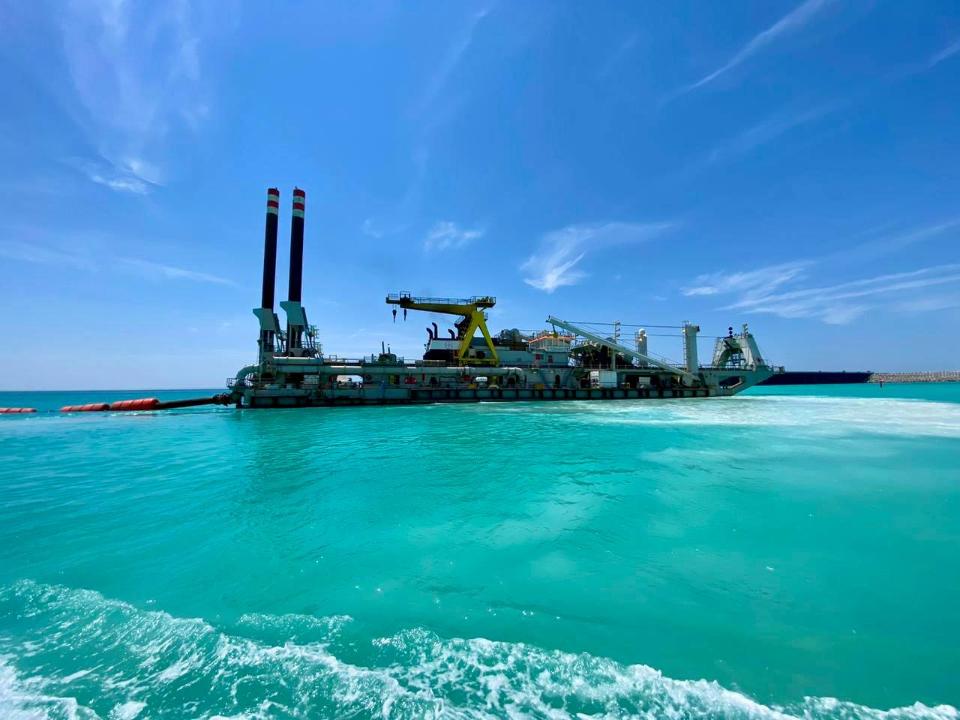
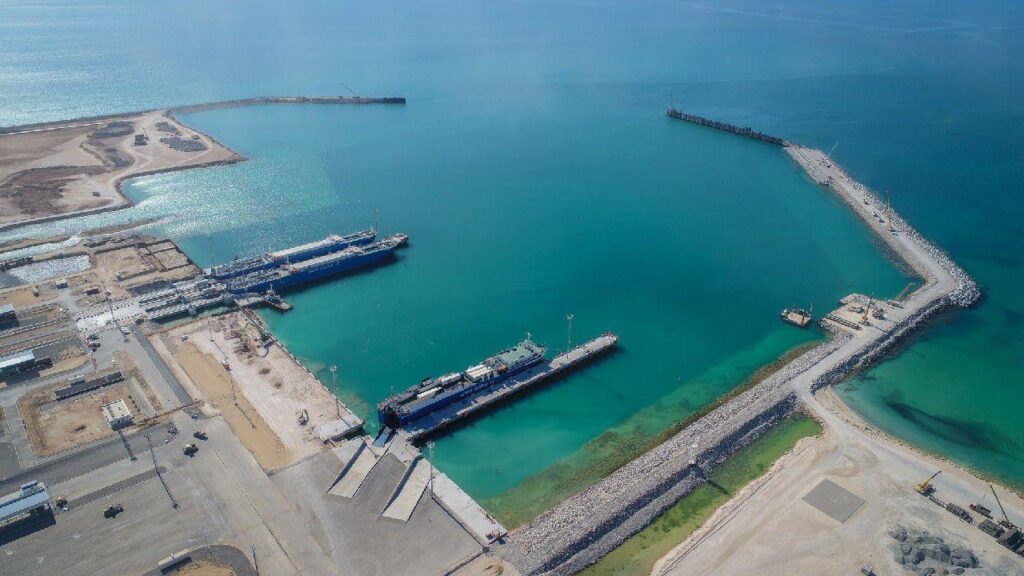
Kazakhstan plans to expand its maritime fleet by building seven new vessels on the Caspian Sea. These vessels will be three tankers, two ferries, and two container ships. The construction of the vessels is part of a broader strategy to develop Kazakhstan's transportation and logistics infrastructure, which will strengthen its position on the Caspian Sea. Today, Kazakhstan's merchant fleet consists of 17 vessels: 10 tankers, four dry bulk carriers, and three container ships. In December 2023, KazMunayGas and Abu Dhabi Ports Group signed an agreement to establish a ship repair and shipbuilding yard in Kazakhstan. This project will provide the necessary base for the repair and construction of new vessels, which will increase the competitiveness of Kazakhstan's fleet on a global level. In addition, Kazakhstan continues to strengthen its ties with Azerbaijan. Tankers have already been purchased to transport oil from Kazakhstan to Azerbaijan for subsequent shipment via the Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan oil pipeline. This cooperation will diversify export routes and ensure the stability of supplies. Turkey has become another significant partner of Kazakhstan in shipbuilding. Under an agreement with Turkish companies, new vessels will be built, providing the country with additional opportunities to develop trade relations in the region. This project will also reduce Kazakhstan's dependence on Russia in shipbuilding, and strengthen its position in the Caspian Sea.