Kazakhstan to Build New International Cargo Airport Near China Border
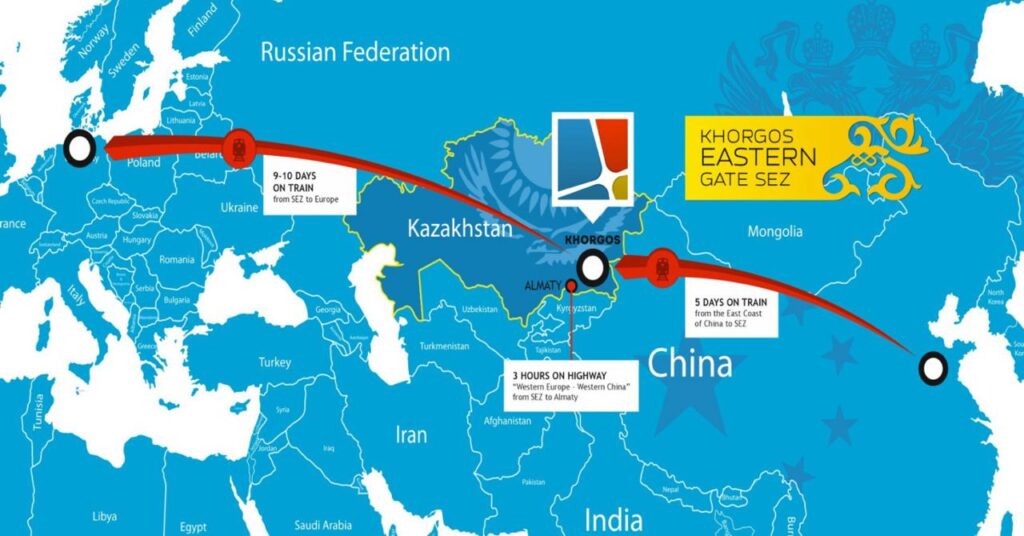
Kazakhstan plans to construct a new international cargo and passenger airport in the Zhetysu region, near the Chinese border, as part of efforts to develop a major multimodal aviation and logistics hub along key transit routes linking China, Central Asia, and Europe. The facility will be located within the Khorgos–Eastern Gate Special Economic Zone (SEZ), a strategic logistics cluster on the New Silk Road. According to Dias Esdauletov, Deputy Akim of the region, the project is one of the most significant and promising investment initiatives currently underway and aims to establish Kazakhstan as a central player in Eurasian trade. The project is being developed by the Kazakh-German joint venture Skyhansa LLP and is coordinated by the Ministry of Transport of the Republic of Kazakhstan. The airport is designed to complement the existing railway and road infrastructure in the SEZ, enabling faster movement of high-value and time-sensitive cargo, and bolstering regional passenger transport and tourism. Once completed, it will integrate rail, road, and air links in a single multimodal logistics system. Construction will be carried out in three stages. The first stage, set for completion by mid-2027, will include the development of core airfield infrastructure, a cargo terminal, a fuel complex, an aviation technical center, and a business center with hotel facilities. It will also integrate the airport with the SEZ’s existing rail and road networks. The second stage will expand the cargo and passenger infrastructure, build additional logistics and storage areas, increase refueling capacity, and attract airline and logistics partners. In the third stage, the airport is expected to evolve into a full-fledged international aviation hub with an expanded route network, full-service and MRO (maintenance, repair, and overhaul) operations, and deep integration with the SEZ’s industrial and commercial zones. Esdauletov highlighted the importance of the Air-Rail-Auto-Air transport model for improving logistics efficiency, particularly for sectors such as e-commerce, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. Seamless transitions between transport modes can dramatically reduce door-to-door delivery times and costs. Kazakhstan has already demonstrated the viability of such multimodal solutions. In 2014, KTZ Express piloted a successful international cargo transit from China to Europe via a rail-air corridor. HP products were shipped from Chongqing to Almaty by rail and then flown to Amsterdam, completing the 9,900 km journey in just seven days. The new airport is expected to ease congestion in the Almaty transport hub and significantly improve cargo throughput capacity in southeastern Kazakhstan. In the medium and long term, authorities anticipate strong growth in both cargo and passenger volumes, driven by increasing transit flows between China, Central Asia, Europe, and the United States, as well as ongoing shifts in global logistics routes. To mitigate risks, the regional government has launched comprehensive preparatory work. Skyhansa has already secured 800 hectares of land within the Khorgos-Eastern Gate SEZ. The project is expected to create approximately 700 jobs.