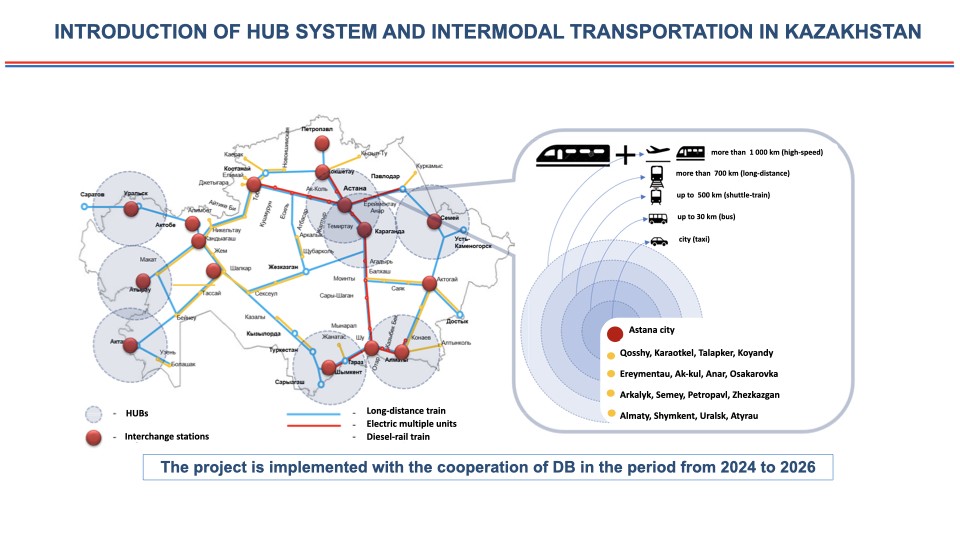
Zhenis Kassymbek, the Akim (governor) of Kazakhstan’s capital Astana, has announced that the city’s first light rail transit (LRT) line will launch by the end of next year, marking a significant milestone in a 13-year-long construction project fraught with delays and controversies. The LRT project, envisioned as a high-speed transport system running on elevated tracks to bypass traffic, began construction in 2011. Initially, the line was slated for completion by 2017 to coincide with the EXPO international exhibition. It was intended to connect the Astana-Nurly Zhol railway station with the capital’s airport. While the railway station opened on time, the LRT project was halted in 2013 due to high costs and concerns over its financial viability. The project was revived in 2015 when Astana’s Akimat signed a construction deal with a consortium of Chinese companies, China Railway International Group Limited and Beijing State-Owned Assets Management Co., Ltd. However, further delays occurred when funds — amounting to over 80 billion tenge ($200 million at the time) — were frozen in the accounts of the now-defunct Bank of Astana. Construction began with the installation of support pillars, but the Chinese contractors abandoned the project due to funding issues. In 2019, Kazakhstan’s investigative authorities intervened. Talgat Ardan, the former head of Astana LRT, and Kanat Sultanbekov, an ex-deputy mayor of Astana, were accused of embezzling nearly 30 billion tenge. This included inflating project costs and awarding overpriced contracts. Both were sentenced in absentia to seven years in prison in May 2023. Despite initial skepticism from President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev, who questioned the project’s ridership potential given its 22-kilometer length and route, the decision was made to proceed. Former Akim Altay Kulginov argued that dismantling the incomplete infrastructure would cost more than completing it. Under Kassymbek, construction has progressed. “The first LRT trains will arrive in August or September next year. We expect to have 15 trains operational by fall, with technical testing by the end of 2024 and full service in early 2026,” Kassymbek stated during a briefing. The elevated tracks are nearing completion, with rail-laying in progress. Signal installation is set to begin in spring. The Akimat anticipates the line will serve approximately 20,000 passengers daily. The fare for LRT rides has yet to be finalized. Kassymbek announced that the pricing would remain affordable. However, he stopped short of providing specifics. In 2017, the proposed fare was 300 tenge per ride, three times the cost of a bus ticket at that time. Current bus fares in Astana range from 110 tenge for regular routes to 250 tenge for express routes. Given the LRT’s total project cost of $1.88 billion, fares significantly higher than bus rates may be needed to achieve profitability. Despite this, the LRT could address pressing issues, such as Astana’s daily traffic jams. Currently, buses are the only public transport option in the city. “We aim to expand roads, increase bridges, and enhance public transport to encourage residents to switch from private vehicles,” Kassymbek said. He also suggested that Turkestan and...