Kazakhstan Intends to Triple Its Hydropower Capacity by 2030
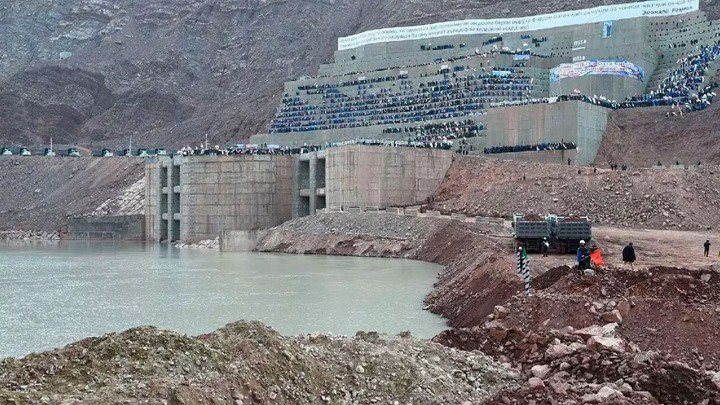
Kazakhstan plans to significantly expand its hydropower capacity over the next five years. By the end of 2030, the country intends to commission new hydropower plants with a combined capacity of approximately 660 MW, nearly tripling the sector’s current installed capacity, according to the Ministry of Energy. At present, 43 hydropower facilities operate in Kazakhstan with a total installed capacity of 313 MW. The implementation of agreements already concluded is expected to raise this figure to nearly 1 GW, substantially increasing the contribution of hydropower to the national energy mix. In 2025, an additional project was added to the portfolio: the 26 MW Korinskaya HPP-2 was commissioned in the Jetisu Region. By the end of the year, total electricity generation from renewable energy sources reached 8.621 billion kWh, of which 1.196 billion kWh was produced by small and medium-sized hydropower plants. Kazakhstan continues to rely on an auction mechanism to attract investment and enhance transparency in the renewable energy sector. In 2025, 500 MW of capacity designated specifically for hydropower projects was offered through competitive auctions. According to the Ministry of Energy, this approach helps reduce project costs and foster a stable investment environment. The highest concentration of renewable energy facilities, including hydropower plants, is located in the southern and southeastern regions, Zhambyl, Almaty, and Jetisu regions. These areas benefit from significant river potential and established infrastructure capable of supporting further generation growth. The ministry states that implementation of the planned projects will diversify Kazakhstan’s energy mix, supply remote areas with stable green electricity, reduce pressure on the main transmission grids, and enhance overall system reliability. As previously reported by The Times of Central Asia, renewable energy accounted for 7% of Kazakhstan’s national energy mix by the end of 2025.