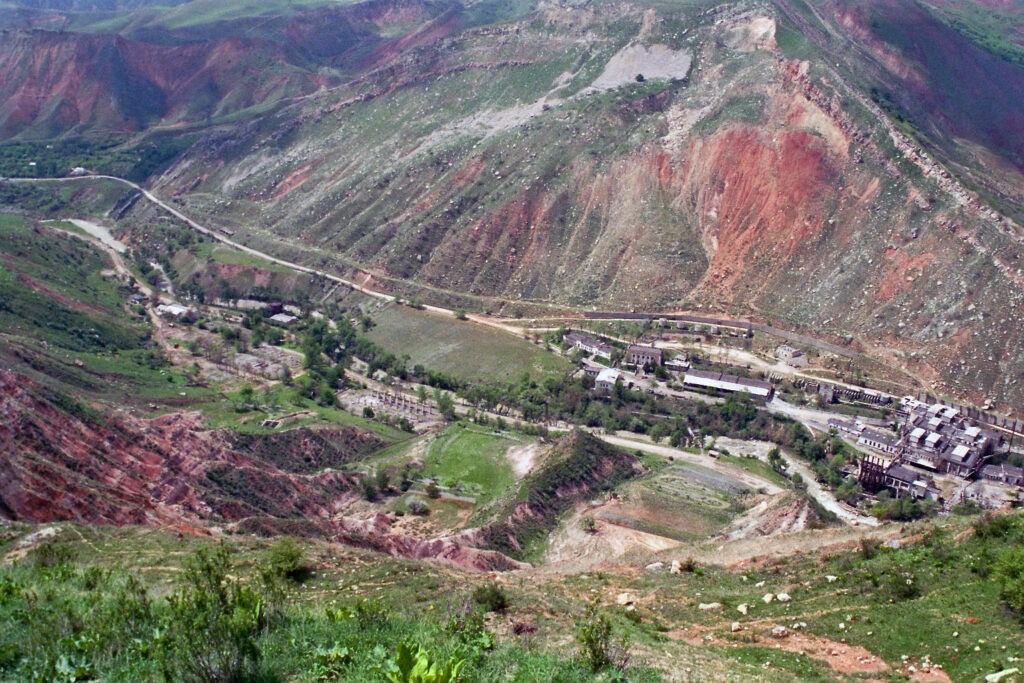
Deputies of the Kyrgyz Parliament have approved a bill lifting the ban on mining uranium and thorium by 69 votes in favor to three against. Parliamentarians are confident that the legislative changes will bring significant economic dividends to the country. The law banning uranium and thorium mining was passed in 2019. At that time, authorities wanted to sell the license to develop a deposit, but faced a significant pushback from residents who feared the project could harm the environment and damage the water table. The result was a complete ban on the entire territory of the Republic. In the Issyk-Kul region of Kyrgyzstan alone, 150,000 cubic meters of radioactive waste were accumulated from uranium mining in the last century. According to the Ministry of Emergency Situations, the country has 92 burial sites, with 23 tailing dumps containing uranium elements. Kyrgyzstan's total volume of poisonous and hazardous substances stands at 2.9 million cubic meters. The notes behind the new bill indicate that alternative sources of income are needed due to severe economic impacts over recent years. However, these activities must strictly comply with environmental norms and standards in uranium and thorium mining. Speaking in parliament, Minister of Natural Resources, Environment, and Technical Supervision, Melis Turganbayev assured deputies that the bill's passage would not harm the environment or the health of Kyrgyz citizens. “For uranium mining to be profitable, a deposit needs 40-50 tons. Kyrgyzstan lacks such reserves. There are occurrences from 0.01 to 0.08% in 83 locations. Our goal is not the uranium, but the associated metals,” Turganbayev said. Authorities plan to mine titanomagnetite, which is accompanied by uranium and thorium. Both elements will be processed at the Kara-Balta Combine in Chui Oblast. Thorium will be stored, while uranium will be sold to other states. Iskhak Masaliyev, one of the three deputies who voted against the bill, reminded his colleagues of discussions in the early 2000s on ecology. However, only now has it been possible to begin to eliminate harmful waste. Doctor of Geological and Mineral Sciences, academician Rozalia Jenchuraeva told The Times of Central Asia that the 2019 law banning mining was “a big folly” as it suspended all waste activities and impacted jobs, leaving hazardous materials lying no more than 20 meters deep are slowly contaminating the soil and water. “If they pull it all out, it will be wonderful. It will clean up the land. This is work for the Kara-Balta Combine. I think the government has decided to develop Kyzyl-Ompol, which is the right thing to do,” Jenchuraeva said. Jenchuraeva believes that Kyrgyzstan has qualified personnel who have previously worked at uranium sites, know how to mine uranium and thorium, and can develop the deposits using their expertise and resources. Earlier, President Japarov met with residents near the Kyzyl-Ompol deposit. “The development of Kyzyl-Ompol will create over a thousand jobs. This mine will become the second Kumtor (gold deposit). The local budget will cease to be subsidized, and the people will get richer,” the president said. Kyzyl-Ompol is...