One Health Nature Conservation Project Launches in Central Asia
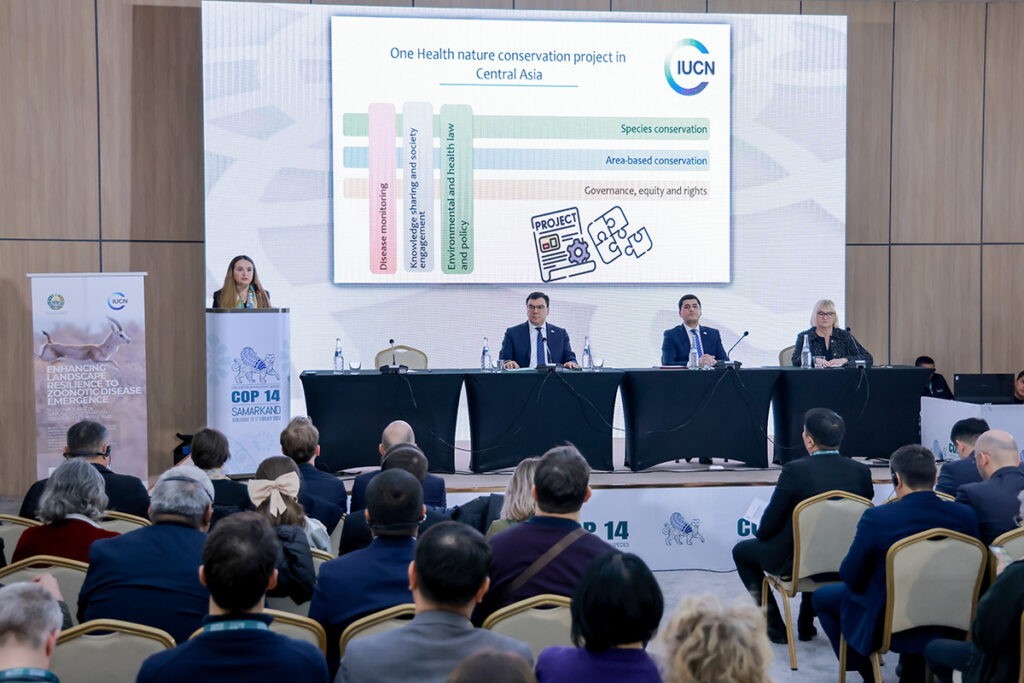
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and its international partners have launched the One Health Central Asia project, aiming to mitigate the risk of zoonoses – diseases that are naturally transmissible from animals to humans – in Central Asia. The new initiative was announced on February 13th at the 14th Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS COP14) in Samarkand, Uzbekistan. The risk of zoonotic diseases in Central Asia is exacerbated by biodiversity loss and changes in human-wildlife interactions. As part of the new initiative, IUCN and national and international partners, including all five Central Asian countries, will implement actions to prevent the emergence and spread of zoonotic diseases, IUCN reported on its website. The experts will work to consolidate a fair and effective regional network of protected and conserved areas, strengthen conservation measures and wildlife management for disease risk mitigation, and promote the latest advancements in zoonosis research and technology. Speaking at the launch ceremony, IUCN’s director general, Dr Grethel Aguilar, said that nature conservation can contribute to mitigating the risk of zoonotic disease outbreaks, and this important new initiative will strengthen the resilience of Central Asian landscapes, bringing numerous benefits to communities. “We will continue to support the governments here to build regional capacity to apply IUCN's tools and standards, including the IUCN Green List, best practices in species management, and the latest advancements in zoonosis research.” Aziz Abdukhakimov, the minister of ecology, environmental protection, and climate change of Uzbekistan, commented that: “Over the past few years we have observed how the spread of zoonotic diseases like COVID-19 can have a global impact. This has resulted in entire countries being demobilized, transportation connections being disrupted, an increase in food security issues, and massive socio-economic consequences. We are committed to expanding regional cooperation for sustainable management of protected natural areas, preserving unique biological diversity, and contributing to the environmental balance in the Central Asian region, which will receive a significant boost through this project on One Health in nature conservation.” Supported by a €11m contribution from the German Ministry for Environment, Nature Conservation, Nuclear Safety and Consumer Protection via the International Climate Initiative, this major regional initiative will spearhead the One Health approach in Central Asia over the next six years. The initiative, entitled Enhancing landscape resilience to zoonotic disease emergence by consolidating nature conservation systems in Central Asia, will focus on the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health. "Obstacles to migration reduce the habitat available to migratory species. This phenomenon has been observed across Central Asia with species such as the Saiga, Wild Ass, and even those with relatively small ranges, like the Bukhara Deer,” said Amy Fraenkel, the executive secretary of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS), one of the international partners of the One Health Central Asia initiative. “In the diminished and fragmented habitats, migratory species of wild animals often find themselves in contact and competition with livestock for pasture and water...