Kazakhstan’s Strategic Stand: Navigating BRICS Amidst Geopolitical Tensions
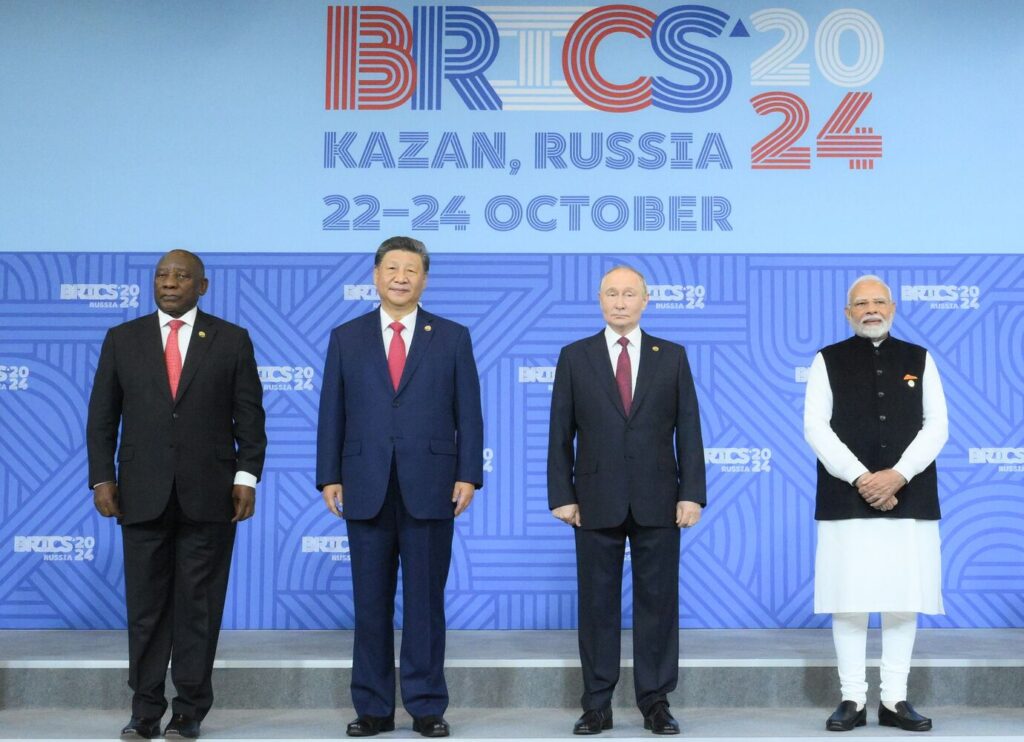
In recent days, BRICS - an intergovernmental organization comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, Iran, Egypt, Ethiopia, and the UAE - has become one of the most critical topics on the Eurasian region's information agenda. Russian propaganda has presented the BRICS summit, which is taking place in Kazan, as a global event. However, the press secretary of Kazakhstan's president, Kassym-Jomart Tokayev, has stated that the republic has no plans to apply for BRICS membership in the foreseeable future, which has caused an adverse reaction in the Russian media, and led to a seemingly retaliatory Russian ban on Kazakhstan's agro-products. The Kazakhstani side, represented by the expert community, has tried to explain that its reasoning is based not only on Astana's national interest, but also on its obligations to its partners in Central Asia. Perhaps the most convincing argument is that the C5+1 mechanism is effective as a format for the region's interactions with the outside world. Therefore, it is not worth breaking this mechanism. No Central Asian country besides Kazakhstan has been invited to join BRICS, but Astana cannot afford to damage the established alliance by creating the conditions for distrust from its neighbors; Central Asia has already gone through a period of distrust. At the same time, rejecting the idea of joining BRICS, where India, Russia, Brazil and China are the founding members, does not unduly affect Kazakhstan's interactions with these powers. Kazakhstan works with China and Russia within the framework of the SCO (Shanghai Cooperation Organisation) and EAEU (Eurasian Economic Union), and has signed multiple partnership and alliance agreements with Beijing and Moscow. In other words, the information hysteria that Kazakhstan will exit Russia's sphere tomorrow and join the "Global West" (a term used in the Russian media) has no basis in reality. At the same time, however, it is evident that most Central Asian countries are trying to distance themselves from Russia as much as possible, maintaining cooperation only along certain economic lines. Even banks in Kyrgyzstan, a republic maximally dependent on Moscow on several essential issues, have stopped working with Russian banks. The Kazakhstan Stock Exchange, meanwhile, recently announced the end of cooperation with the sanctioned Moscow Stock Exchange. Moreover, Rosselkhoznadzor's ban on imports of a wide range of agro-industrial products from Kazakhstan, if not a response to the refusal to join the BRICS, clearly hints that behind the scenes, economic relations between Astana and Moscow are not all that smooth. Another argument against joining BRICS was voiced not just within Kazakhstan, but also by Russian experts. Despite the organization's purportedly representative nature, which includes countries with a combined population of 3.5 billion people (45% of the Earth's population), the association has no structure. Russian analysts opposed to the Kremlin believe that BRICS is a club where one can come, sabre-rattle at the West, conclude bilateral agreements, and forget about everything until the next summit. No coordinating center monitors the implementation of any agreements reached. BRICS was conceived as an intercontinental organization, uniting similar economies in volume and GDP. Thus, it initially included Brazil, representing...