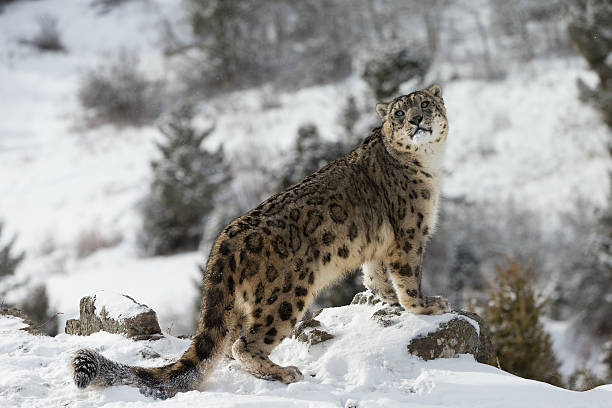
According to the state gold mining company Kumtor, operating near the Sarychat-Ertash high-mountain reserve, the number of red-listed animals has increased significantly as a result of ecological improvements to their environment. Local ecologists, however, believe that the data has been intentionally exaggerated.
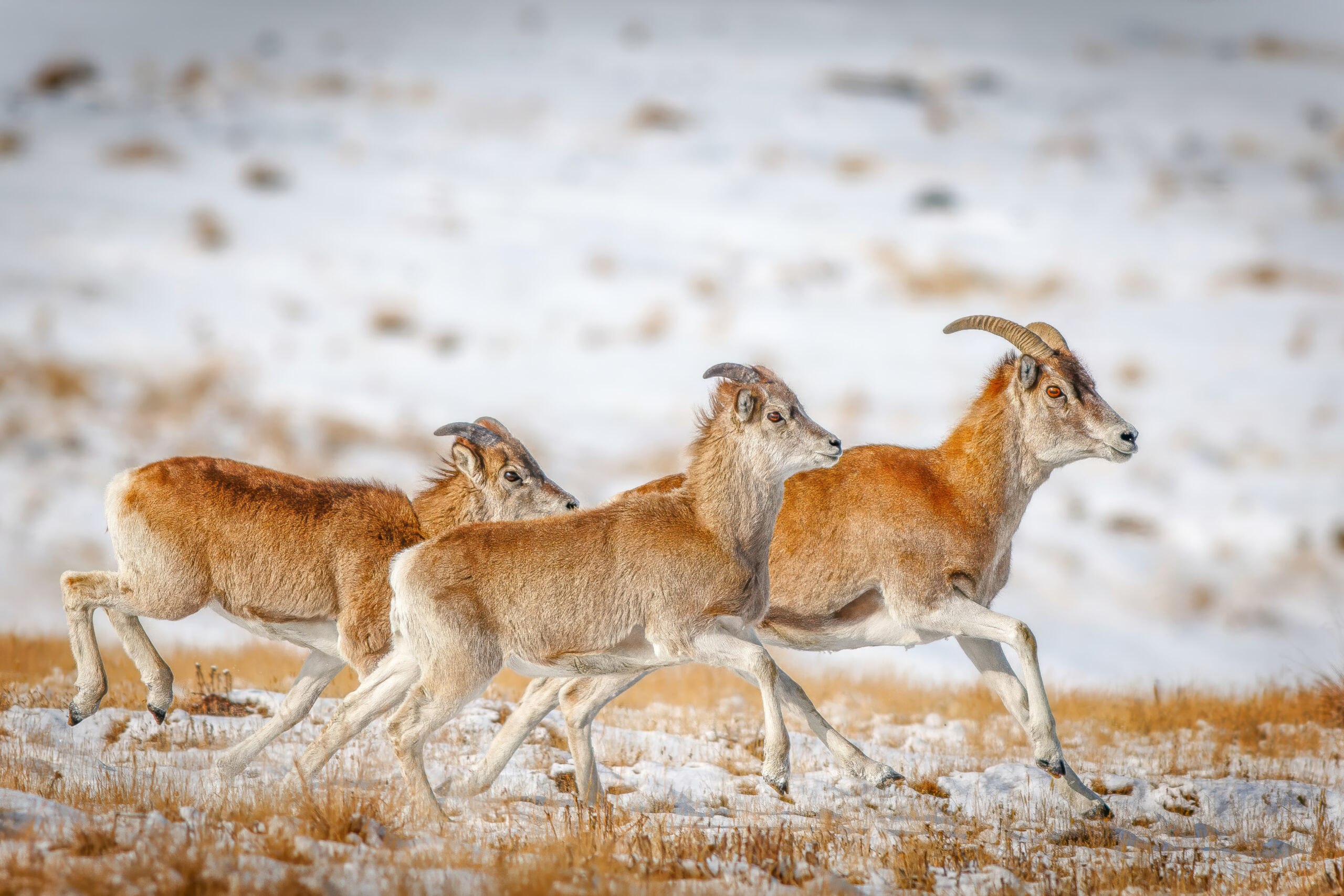
In its report, Kumtor said, “Annual monitoring of the state of biodiversity, conducted by the company, allows us to accurately track the ecological situation on the ground. Care for ecology and the environment is also evident in the increasing numbers of argali, ibex, and snow leopards. For example, the number of argali in the Sarychat-Ertash reserve increased from 750 to 2,500, making it the country’s largest population. Capricorns, argali, and snow leopards have also increased in number.”
Environmental scientists at the National Academy of Sciences of Kyrgyzstan (NAS KR) state that whilst a rough count of red-listed animals in hunting farms and state nature reserves shows an increase in all argali and snow leopard subspecies, the state authorities have not provided an accurate calculation for 14 years.
“All hunting farms of the republic every year give the state structures data on the number of argali, ibex, and other red-listed animals. According to their data, the number of animals is growing, but how much this data can be believed remains a question. They are interested parties and may present distorted data,” Askar Davletbayev, an ecologist with the National Academy of Sciences, told The Times of Central Asia.
In Kyrgyzstan, the state protects argali and snow leopards. During the hunting season, however, authorities issue a yearly license to shoot the animals. A popular and lucrative sport, it attracts visitors from all over the world who willingly pay around 10 thousand dollars to bag an argali.
According to eco-activist Vlad Ushakov, the fact that predatory animals living on high mountain ranges have begun to descend to the lower reaches to hunt, has also impacted the figures.
“This does not speak of an increase in snow leopards but rather a lack of prey; the forage base has been undermined. In the gorges, where wild animals traditionally used to graze, there is now mass grazing. The snow leopard will not voluntarily change its natural habitat. Ten years ago, we were told there were 300-350 leopards in Kyrgyzstan; today, the same figures apply. Perhaps these are just invented figures with no basis,” Ushakov explained to TCA.