Waiting for Cubs: How Almaty Zoo is Helping Save the Amur Tiger Population
Almaty Zoo is helping to replenish the Amur tiger population under an international conservation program. The Amur tiger population is still declining, and the main challenge for scientific foundations from different countries is breeding new cubs.
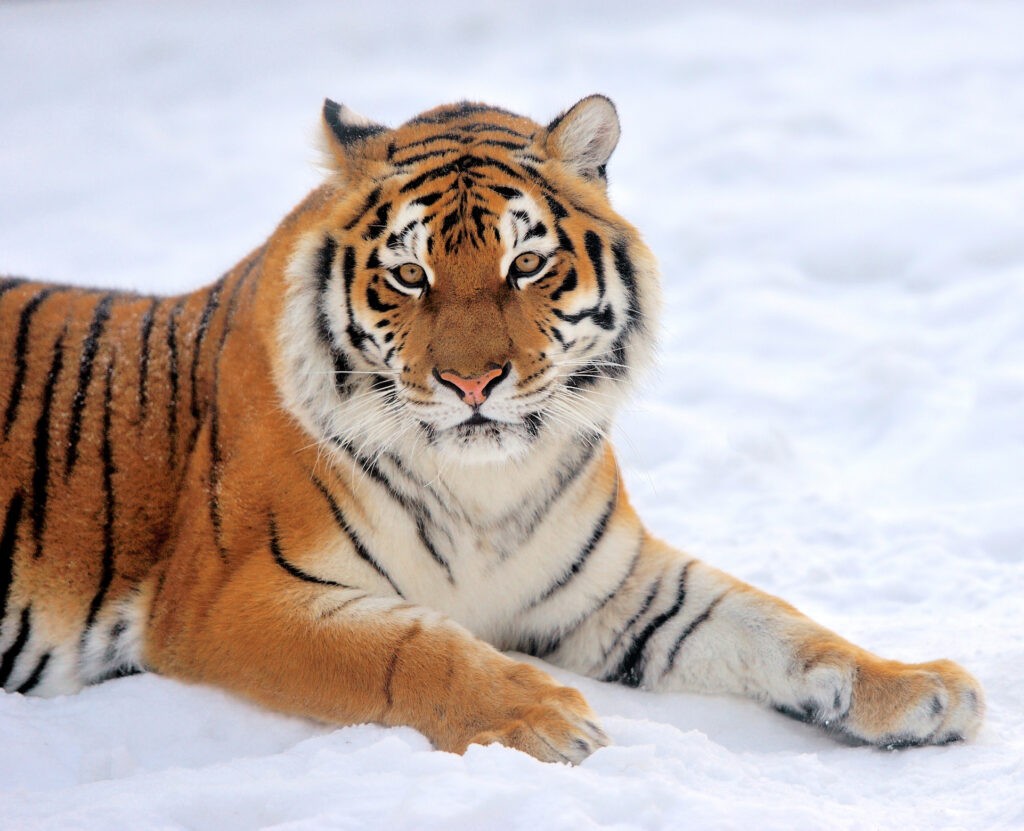
Almost 400 species of animals live at the Almaty Zoo. Among them are llamas, chimpanzees, hippopotamus and tigers, with the latter comprising a family of nine individuals. The clan is headed by 13-year-old Urman, who arrived in Kazakhstan at one-year-old from the Perm Zoo in Russia by way of an international conservation program.
“The main objective of the program is to preserve the genetic diversity of animals in the northern part of Eurasia and their reproduction, including in captivity. That’s why we carefully searched for a mate for Urman, and not so long ago we managed to bring in a tigress, Tasha, from Moscow,” said Akzhami Rakhimova of the Almaty Zoo.
Now, staff are carefully monitoring the pair’s behavior and diet so they can give reproduce.
The last time tiger cubs were born at the zoo was three years ago. They were given the names Aya, Zoya, Maya, and Sherkhan. Zookeepers celebrate the birthdays of their charges, and very soon the birthday of Bentley, who arrived from the circus in Astana, is coming up. He will be five-years-old, and since he’s already reached puberty, he’ll soon need a mate.
The staff note that the zoo is home for these animals which don’t know life beyond captivity, as they either came from the circus or were born here. The tigers are quite accustomed to the attention of visitors and to eating on schedule.