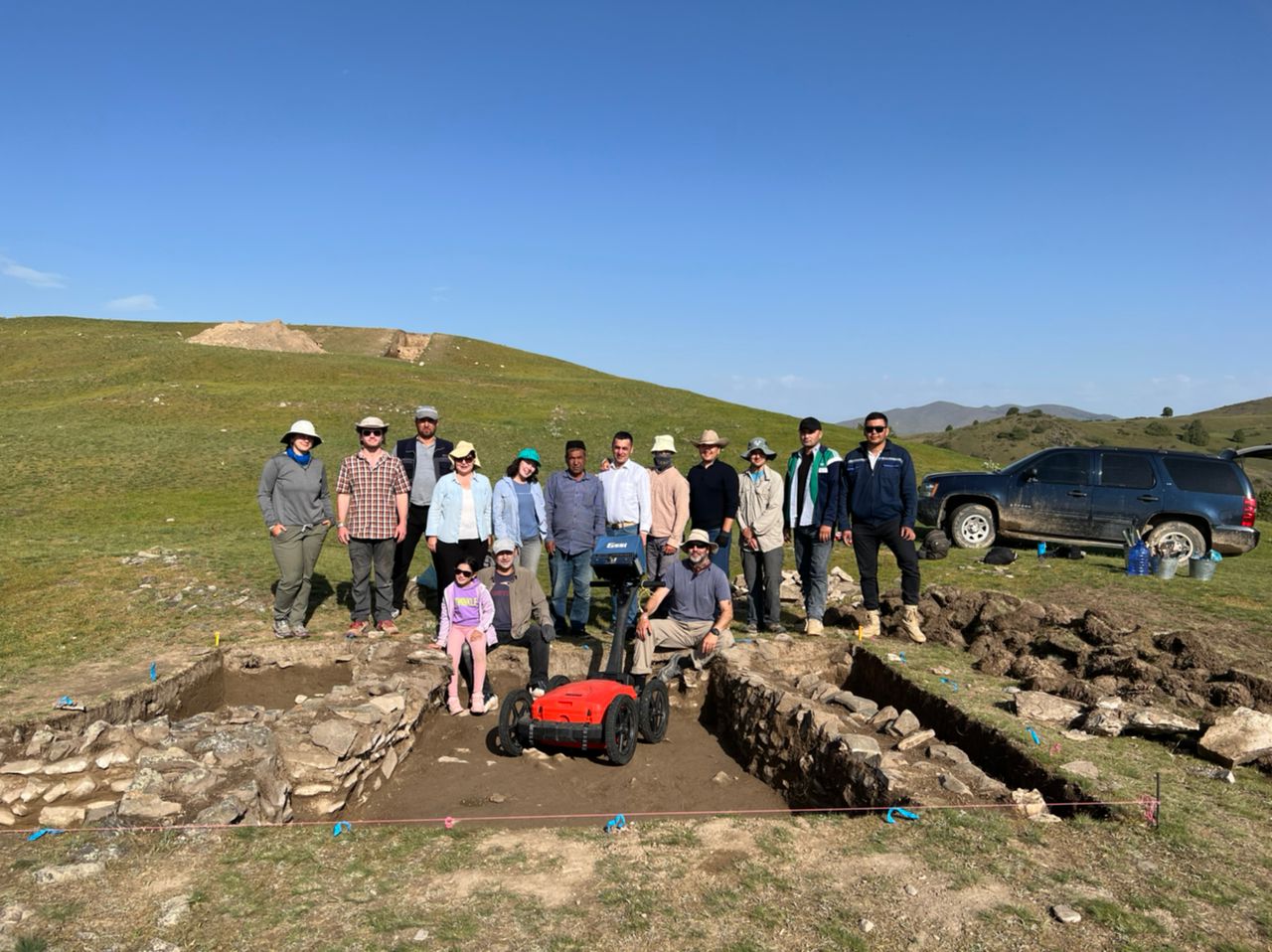
Aided by laser-based technology, archaeologists in south-east Uzbekistan, have discovered two lost cities that once thrived along the Silk Road from the 6th to 11th centuries AD.
As reported by Reuters, one was a center for the metal industry, and the other, indicates early Islamic influence. Located some five kilometers apart, these early fortified outposts are among the largest found on the mountainous sections of the Silk Road.
“These cities were completely unknown. We are now working through historical sources to find possible undiscovered places that match our findings,” said archaeologist and lead author of the report, Michael Frachetti of Washington University in Saint Louis.
The researchers state that the most expansive of the two, Tugunbulak, covered about 300 acres (120 hectares) and in existence from around 550 to 1000 AD, boasted a population of tens of thousands. As such, it was one of the largest cities of its time in Central Asia, rivaling even the famed trade hub Samarkand, situated about 110 km away, and according to Frachetti, many times larger and more enigmatic than other highland castles or settlements that have been documented in high-elevation Central Asia.”
The other city, Tashbulak, inhabited from around 730-750 to 1030-1050 AD, was only a tenth the size of its neighbor, with a population perhaps in the thousands.
After discovering the first signs of the cities’ existence, archaeologists employed drone-based lidar – a technology that floods the landscape with lasers to measure the topography – to map and establish the size and layout of the sites. Findings revealed highly defined structures, plazas, fortifications, roads, homes, and other urban features.
An initial dig at one of Tugunbulak’s buildings, fortified with thick earthen walls, uncovered kilns and furnaces, suggesting it was a factory wherein, metalsmiths turned local iron ore into steel. During the 9th and 10th centuries, the region was known for its steel production and researchers are now analyzing slag found on-site to confirm their hypothesis that in addition to trade in livestock and related products such as wool, the metal industry may have been a central feature of Tugunbulak’s economy.
According to Franchetti, “Tugunbulak, in particular, complicates much of the historical understanding of the early medieval political economy of the Silk Routes, placing both political power and industrial production far outside the regional ‘breadbaskets’ such as Samarkand.”
As stated in the report, Tashbulak lacked the industrial scale of Tugunbulak but boasted an interesting cultural feature: a large cemetery that reflects the early spread of Islam in the region. Its 400 graves—for men, women, and children—include some of the oldest Muslim burials documented in the area.“The cemetery is mismatched to the small size of the town,” said Frachetti. “There’s definitely something ideologically oriented around Tashbulak that has people being buried there.”
Tugunbulak and Tashbulak are especially remarkable given their altitude, which is roughly comparable to that of the later Inca citadel of Machu Picchu in Peru, and as noted by Frachetti, “The key finding of this study is the existence of large, fortified, and planned cities at high elevation, which is still rare but much more exceptional in ancient times.”