Kyrgyzstan Minister Says Case Against Media Workers Not About Politics
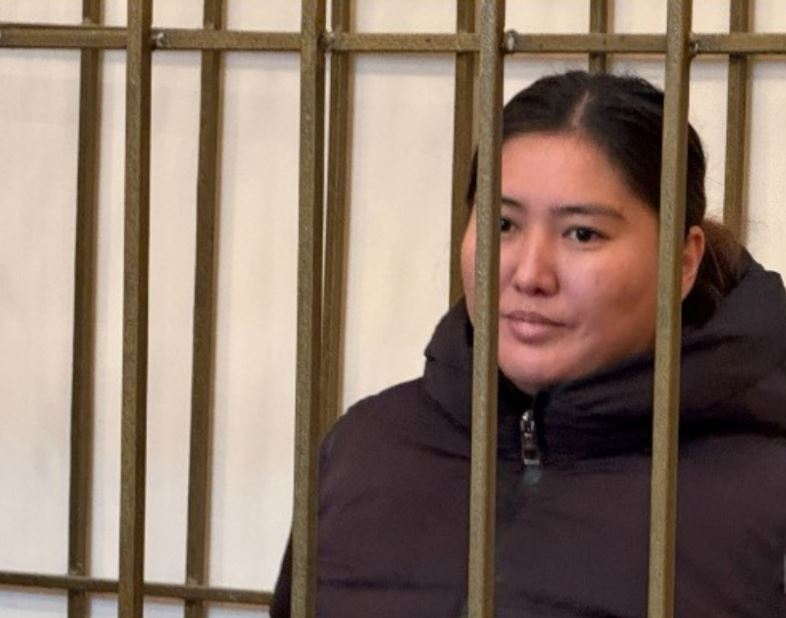
BISHKEK, Kyrgyzstan – Kyrgyzstan is pushing back against international criticism of a high-profile prosecution of media workers, saying the case is not politically motivated and that those facing charges of inciting mass unrest are poorly educated people masquerading as journalists. Minister of Internal Affairs, Ulan Niyazbekov, said the case against 11 former and current workers for media outlet Temirov Live stems from the publication of false information that flouts the basic rules of journalism. Free speech advocates say Kyrgyzstan is clamping down on what was once a relatively permissive environment for the media. “If they continue to write everything that comes to their mind without facts and evidence, just saying that they are journalists, then we will arrest them,” Niyazbekov said in an interview with Kabar, Kyrgyzstan’s national news agency. He said most of the people accused in the Temirov Live case are “bloggers,” not journalists. “They spread false information because they don't have education and make people panic. And there is no need to make noise about them saying that they are journalists,” he said. The minister’s comments were published on Thursday, two days after a court in Bishkek ordered the transfer of four of the journalists from prison to house arrest. Four others accused in the same case remain in pretrial detention. If convicted, they could be sent to prison for years. Temirov Live is a YouTube-based outlet that has published and broadcast reports on alleged corruption by senior officials. It was founded in 2020 by Bolot Temirov, who was expelled from Kyrgyzstan in 2022. He has said the ongoing case against his colleagues is in retaliation for Temirov Live’s investigations into alleged government misconduct. In an interview with Kabar, Niyazbekov noted that there were potential penalties in Europe and the United States for journalists who spread false or unconfirmed information. “They don't accuse someone without proof,” he said. “If someone tries to slander someone or spread false information about the activities of the authorities, they will be brought to court and pay a large compensation or be imprisoned.” The government in Kyrgyzstan tolerates criticism but its “only demand” is that critics “gather evidence or make the information very precise and then release it to the public,” Niyazbekov stated.