Afghan Canal Will Divert Water from Uzbekistan
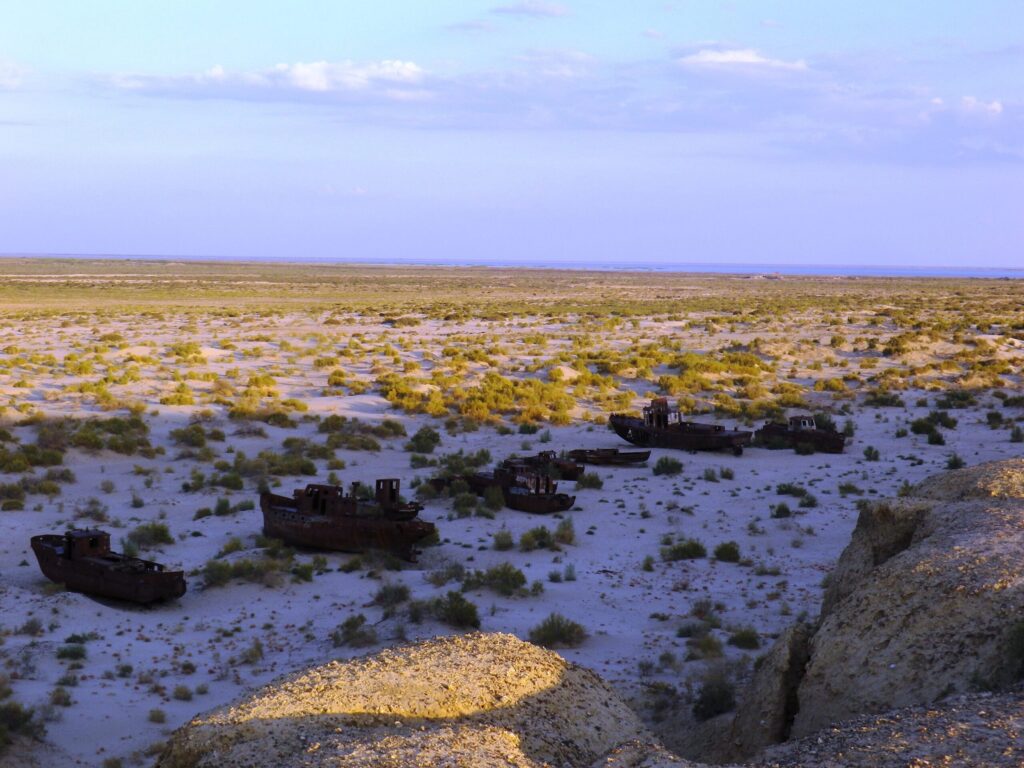
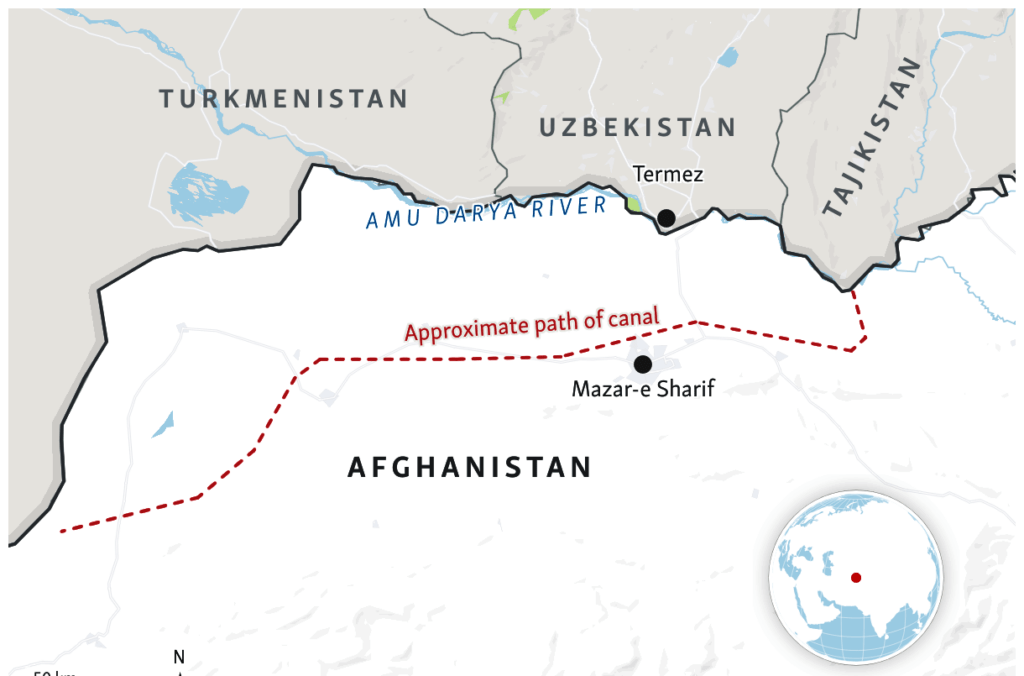
Afghanistan has begun construction of the second phase of the Qosh Tepa Canal, which will divert water from the Amu Darya River and may have an adverse effect on agriculture in downstream Uzbekistan. The Taliban announced that construction work on the second phase, which stretches from Dawlat Abad District of Balkh Province to Andkhoi District of Faryab Province, began on February 20th, Afghan broadcaster TOLOnews reported, adding that the 198-km first phase of the canal is now complete and construction of the 177-km second phase will take 12 months. The canal is expected to convert 550,000 hectares of desert into farmland in northern Afghanistan. The Taliban-led government of Afghanistan has made the Qosh Tepa Canal a priority project and its construction started in early 2022. However, neighboring Uzbekistan, the main downstream country in the Amu Darya basin, has expressed concerns that the canal will have an adverse effect on its agriculture. In September 2023, Uzbekistan’s President Mirziyoyev stated that the canal could “radically change the water regime and balance in Central Asia.” Speaking at a meeting of the Council of Heads of the Founder States of the International Fund for Saving the Aral Sea, Mirziyoyev warned that a “new participant in the water use process has appeared in our region.” Mirziyoyev proposed the formation of a joint working group to study all aspects of the Qosh Tepa Canal and its impact on the water regime of the Amu Darya River with the involvement of research institutes of the Central Asian countries. A Eurasian Development Bank’s (EDB) study, “Efficient Irrigation and Water Conservation in Central Asia,” released in November 2023, emphasized the need to mitigate the anticipated decrease in the flow of the Amu Darya River from Afghanistan. EDB analysts forecast that by 2028, the combined effects of climate change, low-water periods and the commissioning of Qosh Tepa Canal in Afghanistan will result in acute water shortages in Central Asia, estimated to be between 5 and 12 km3. With the launch of the canal provisionally set for 2028, its expected water intake from the Amu Darya will be up to 10 cubic kilometers. A reduction in the Amu Darya flow will have an impact on the entire Aral Sea basin. As a result, from 2028, Central Asia will face a chronic water shortage, Evgeny Vinokurov, chief economist of the EDB warned.