UK Expands Strategic Engagement in Central Asia Amid Growing Global Competition
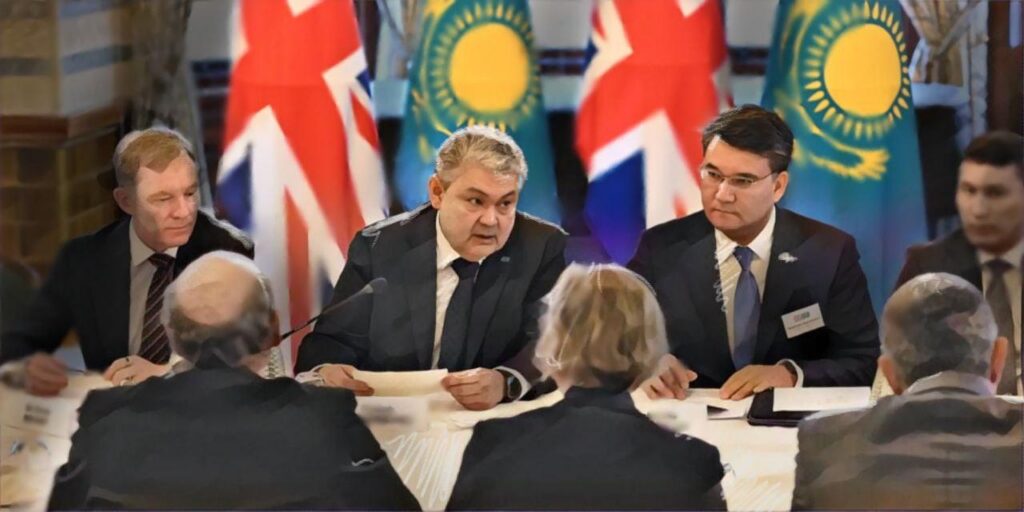
The world’s largest economies have recently increased their focus on Central Asia. The United Kingdom, alongside the U.S., the European Union, and China, is seeking to strengthen partnerships in a region that was previously not among its top foreign policy priorities. Britain Replicates an Established Format Throughout the years of independence, Kazakhstan and its regional neighbors were often perceived as operating within Russia’s sphere of influence. The war in Ukraine and broader geopolitical shifts have altered international attitudes toward Central Asia. Major powers are now intensifying dialogue with the region, with particular emphasis on economic cooperation. At the end of February, foreign ministers met in London under the Central Asia-UK (CA5+1) format. Although this was the first meeting of its kind in the British capital, the format mirrors similar mechanisms already used by the U.S., the European Union, Russia, China, and Japan. Participants noted that the CA5+1 format has proven to be an effective mechanism for structured and substantive engagement with external partners. The regional agenda is addressed comprehensively, reflecting Central Asian priorities while creating additional opportunities to advance economic initiatives and implement joint projects. Particular attention has been paid to trade diversification, industrial cooperation, sustainable infrastructure development, and unlocking Central Asia’s potential in critical minerals and renewable energy. The meeting also covered economic growth prospects, key challenges facing Central Asian economies, and the expansion of trade and investment. Logistics was a central topic, including the development of the Trans-Caspian International Transport Route, widely known as the Middle Corridor. British Foreign Secretary Yvette Cooper emphasized the strategic importance of Central Asia as a dynamically developing region characterized by sustained economic growth, expanding regional cooperation, and a growing role in international affairs. According to the British participants, the region’s countries are pursuing a pragmatic approach, strengthening connectivity and expanding their participation in shaping a modern architecture of economic and political cooperation. Education and Finance Interest in British education continues to grow across all five Central Asian countries. Four branches of British universities are operating in Kazakhstan, and nearly 6,000 students have earned British degrees through the Bolashak international scholarship program. Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan have announced plans to establish international financial centers modeled on the Astana International Financial Centre in Kazakhstan. British Ambassador to Uzbekistan Timothy Smart said that work is underway to create an international financial center in Tashkent based on international arbitration standards. Like the Astana model, the new center will operate under English common law. British Ambassador to Kyrgyzstan Nicholas Bowler highlighted London’s role in assisting with legislation for the International Dispute Resolution Center, which will operate under English law and be located in the Issyk-Kul region. Greater participation by Central Asian companies on the London Stock Exchange is also anticipated. Logistics and Resources British diplomats have placed particular emphasis on cooperation in critical minerals, a priority within the United Kingdom’s global strategy. Projects are underway across the region, accompanied by new agreements and industrial partnerships. Agreements have reportedly been reached between the Kazakh producer Zhezkazganredmet and the British...