In recent years, Korean culture – including K-pop and doramas (dramas) – has gained incredible popularity in Kazakhstan. It has had a significant impact on young people, offering not only entertainment, but also support, motivation, and new opportunities to socialize and express themselves. To better understand how Korean culture is influencing life in Kazakhstan, TCA talked to young people about their stories and experiences.

Image: TCA
Alua, 22, computer club administrator
For me, as an insecure teenager, K-pop and doramas have been a tremendous support and help in shaping my personality. Songs about self-love, with words of encouragement and motivation give many teens a foothold they often can’t get from their environment. The doramas teach us and show us that nothing is impossible, that everything is in our hands. They also show young girls what healthy relationships should look like. That’s what I love about Korean culture, the lack of gender boundaries and the promotion of healthy attitudes. I think this kind of influence has a great effect on the youth of Kazakhstan.
Doramas are television series produced in South Korea and other Asian countries. They cover a wide range of genres: romance, drama, comedy, sci-fi, historical subjects, and more. Doramas are known for their high-quality productions, plot twists, and colorful characters.

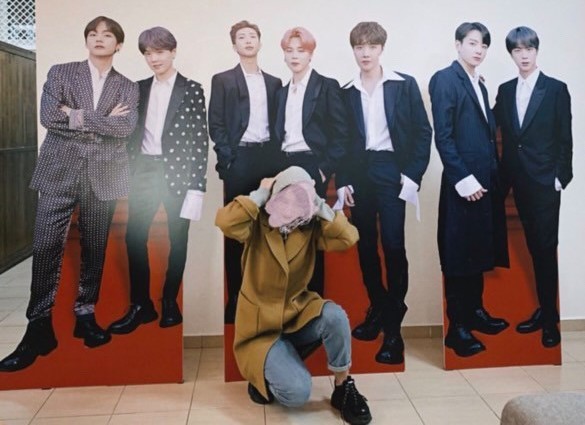
Image by Nastya, from the official BTS film festival in Kino Park, Astana
Nurlan, 19, student at a pedagogical faculty
I like Korean culture because of its unconventionality. For example, K-pop groups such as BTS have always fought against male stereotypes and I’m inspired by it. I think it’s really great, because in Kazakhstan there are big problems with the perception of gender roles. In addition to male stereotypes, they are also breaking down female stereotypes through female groups like BLACKPINK, who present themselves as confident girls who are not afraid of getting their own way.
Also in Kazakhstan, many convenience stores like the Korean 7/11 are opening up where you can eat noodles and tokpoki, and sit with friends, just like in the doramas. I really like it, and I’m happy that Korean trends that are reaching us in Kazakhstan.

Image: TCA
Sarah, 21, store administrator and student
I started getting into Korean culture back in 2010, when my sister showed me the dorama Boys More Beautiful Than Flowers. After that, K-pop and doramas helped me not to get discouraged during difficult moments, offering an interactive culture that nurtured a sense of love and support. Even if it wasn’t fashionable then and I was made fun of, K-pop kept me going.
Now, however, it’s a worldwide phenomenon, and that’s nothing short of heartwarming. So many people around the world have discovered a whole new genre of music, movies, TV series and things in the Korean media space, such as albums and photocards, fan-sites, merch, and concerts. Doramas and shows like Running Man and Apartment 404 have become my favorite part of celebrity promotion in Korea.
K-pop (Korean pop music) albums usually include not only CDs, but various extras that make them unique and appealing to fans, such as photobooks, photocards, posters with images of the band or individual members, stickers, and scrapbooks for fans to decorate or create their own collections.

Image: Nastya, work from Korean language lessons
Amir, 21, social media marketing specialist
I’ve definitely noticed the influence of Korean culture on Kazakhstan. More and more teenagers are into it, and I see positive aspects to it. I especially like manhwa, but I’m less interested in K-pop and doramas.
Manhwa are Korean comic books or graphic novels. They are similar to Japanese manga and Chinese manhua, but have their own unique characteristics. Manhwa are often published online, making them easily accessible to a wide audience. Stories in manhwa can cover a variety of genres, including romance, sci-fi, fantasy, adventure, horror, and more.
Image Nastya, work from Korean language lessons
Nastya, 20, architecture student
My love for K-pop started in 2017 with the song Mic Drop by BTS (feat Steve Aoki). By chance, I came across a BTS playlist on YouTube, and since then I became fascinated with not only the music, but Korean culture. I became interested in what my idols ate, where they lived, and what they did. During the same period, I started taking Korean language classes where I was introduced to other groups such as Stray Kids, Bigbang, Twice, and Monsta X. I wanted to watch concerts and broadcasts without needing subtitles.
After that, I started attending events at the Korean Cultural Center, so Korean culture became a part of my life. I can no longer imagine my life without watching my favorite doramas, listening to songs, and cooking my favorite dishes. In 2019-2020, I had a bad period in my life, but I was helped by the music and inspirational speeches of BTS band leader, Kim Namjoon.
Because of this, my family often gives me albums by my favorite bands, and my friends share my interests, so I draw cards and stickers for them. We also often go to ARMY gatherings in Astana, watch concerts, movies, and visit themed cafes.
ARMY is a fan club of the South Korean group BTS. The name ARMY is an acronym that stands for “Adorable Representative MC for Youth”.
Korean culture continues to have a growing impact on young people in Kazakhstan, offering opportunities for self-expression and emotional support, and showing how culture can connect people.











