Central Asian Leaders Arrive in Azerbaijan for UN COP29 Climate Summit
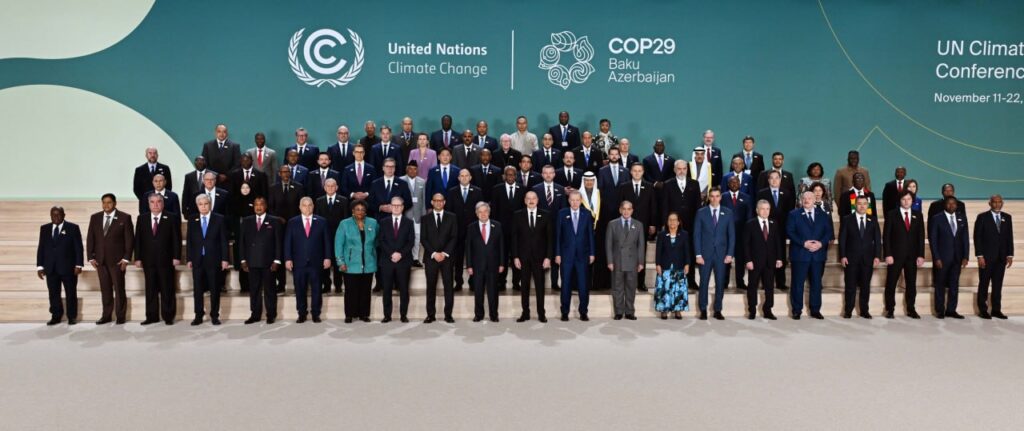
The 29th session of the Conference of the Parties to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (COP29) opened in Azerbaijan's capital Baku on November 11, drawing approximately 50,000 participants, including government representatives, politicians, investors, and environmentalists from 198 countries. Kazakh President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev attended the Summit, where he was welcomed by Azerbaijani President Ilham Aliyev and UN Secretary-General António Guterres. Tokayev will open the plenary session and hold talks with various heads of state, as well as representatives of international organizations and businesses. Kyrgyz President Sadyr Japarov has also arrived at the conference and is scheduled to address the opening session on November 12. He will participate in the special session “High-Level Dialogue: Advancing the Mountain Agenda and Mainstreaming Mountains and Climate Change,” organized by Kyrgyzstan with the support of Azerbaijan and Mongolia. This discussion will also feature Mongolian President Ukhnaagiin Khurelsukh, Nepali President Ram Chandra Poudel, and representatives of international organizations. Russia is represented at the summit by its Prime Minister Mikhail Mishustin. Additionally, representatives of the Taliban, which the UN does not recognize as the legitimate government of Afghanistan, have been included in the delegation for the first time. Armenia, however, has not yet confirmed its participation due to ongoing territorial disputes with Azerbaijan. The Summit is being held at the Baku Olympic Stadium, with sessions set to conclude on November 22. COP29 has been termed a “finance summit” due to its primary focus on financing developing nations in the fight against climate change. Delegates are also working to establish a framework to improve national emissions reduction programs.