85-Million-Year-Old Dinosaur Fossils Discovered in Tajikistan’s Sughd Region
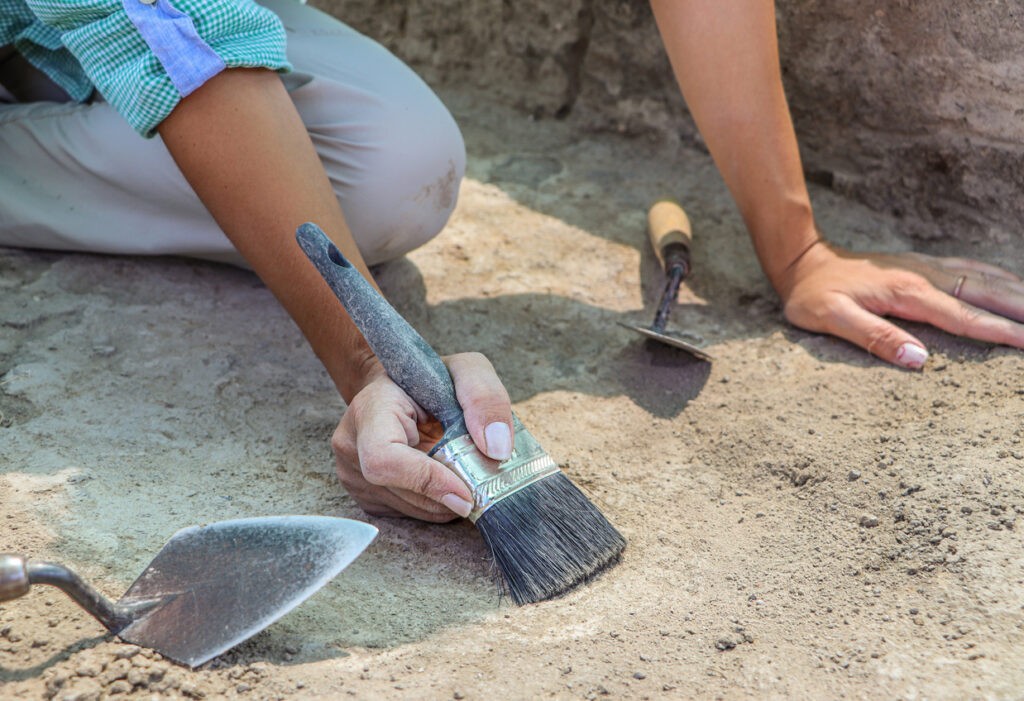
Dinosaur fossils estimated to be 85 million years old have been discovered in Tajikistan’s Sughd region. The excavation took place in the village of Kansai, a renowned paleontological site known for its rich array of prehistoric animals, including ancient lizards, turtles, crocodiles, amphibians, and fish from the Cretaceous period.
The expedition, organized by Russian and Tajik scientists, builds on Kansai’s long-standing significance in paleontology. In the 1960s, Soviet scientist Anatoly Rozhdestvensky and his team uncovered numerous dinosaur remains, including a therizinosaur femur. In the 1980s, Lev Nesov identified traces of mammals from the Cretaceous period. This year, a team led by Associate Professor Pavel Skuchas from St. Petersburg State University has expanded research in Kansai, focusing on smaller vertebrates. Tajik researchers, including Umed Nabiev, a master’s student in paleontology, and ecologist Gafurjon Karimov, joined the excavation.
The fossils were excavated from the walls of a large canyon containing Upper Cretaceous sediment layers, where the team found remains of lizards, salamanders, frogs, and fish. “We used a washing technique to carefully extract even the smallest bones and teeth,” Nabiev explained, noting that a special adhesive was applied to the rock to protect these fragile finds.
Among the larger discoveries were crocodile and turtle shells, as well as the bones of an 85 million-year-old dinosaur. Further research will determine which parts of the dinosaur’s body these bones belonged to. The excavation is set to resume next May, and scientists plan to explore new canyon sections previously mined for cement production.
“Previously, the remains of large animals have been studied quite well, while the remains of smaller animals, such as amphibians and reptiles, have been neglected. In our next expedition, we will also search for small vertebrates,” Nabiev added.
Tajikistan has seen several significant archaeological discoveries in recent years. In 2023, artifacts unearthed at the Oshkhon site in the Eastern Pamirs indicated human presence dating back about 14,000 years.
In 2021, a joint Tajik-German expedition in the village of Khushdilon (Torbulak) near Danghara district uncovered the remains of a Hellenistic sanctuary dating from the 3rd to 1st centuries B.C. These findings continue to expand the historical and cultural understanding of the region.