Three wild horses have been transported from the Prague Zoo to the vast grasslands of Kazakhstan, restoring the endangered species to one of its natural habitats after an absence of a century.
A Czech military plane helped to deliver the Przewalski’s horses to the “Golden Steppe,” or Altyn Dala, in central Kazakhstan, where they will stay for a while in enclosures to get used to conditions in their new environment. The Czech Ministry of Foreign Affairs said it co-funded repairs to the enclosures after damage caused by recent flooding in the Central Asian country.
“Congratulations to all those involved in these huge efforts to return these wild horses to the steppes of Kazakhstan,” said the Altyn Dala Conservation Initiative, a multinational partnership that is working to restore the Kazakh steppe ecosystem. It said on Tuesday that another group of the wild horses, which are named after the Russian geographer who identified the species in 1881, are on their way from Tierpark Berlin, a German zoo.
Przewalski’s horse is “the last genetically wild horse on Earth” and its Russian namesake first came across the species in Mongolia, according to the multinational conservation group. The species vanished from the wild in the 1960s. But several European zoos kept some of the horses, saving the species from extinction, and reintroductions into the wild began in the 1990s, first in China and then in Mongolia.
The Prague Zoo is leading the relocation project in Kazakhstan, which aims to introduce a total of eight Przewalski’s horses to the steppe in the first year and several dozen horses over the next five years. Some of the wild horses will also come from Hungary’s Hortobagy National Park, which has the largest group of Przewalski’s horses outside Mongolia, as well as Nuremberg Zoo in Germany.
The reintroduction center for the horses is located in the Torgai steppe, which lies within a network of linked nature reserves that total 40,000 square kilometers, according to the Frankfurt Zoological Society, a partner in the Altyn Dala Conservation Initiative. The initiative, in turn, is led by the Association for the Conservation of Biodiversity of Kazakhstan.
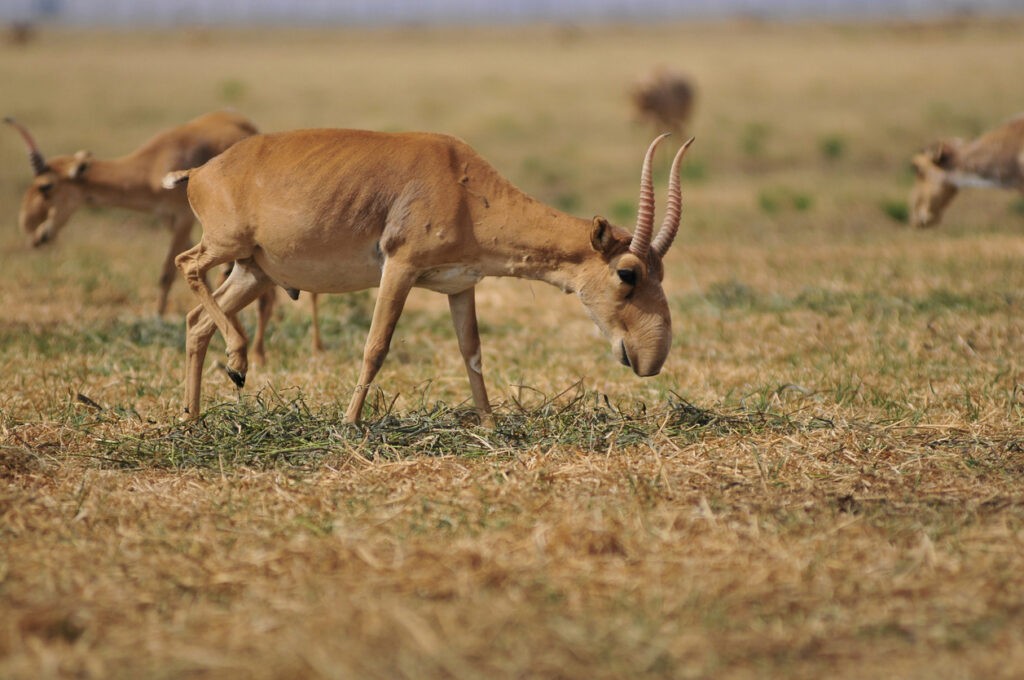
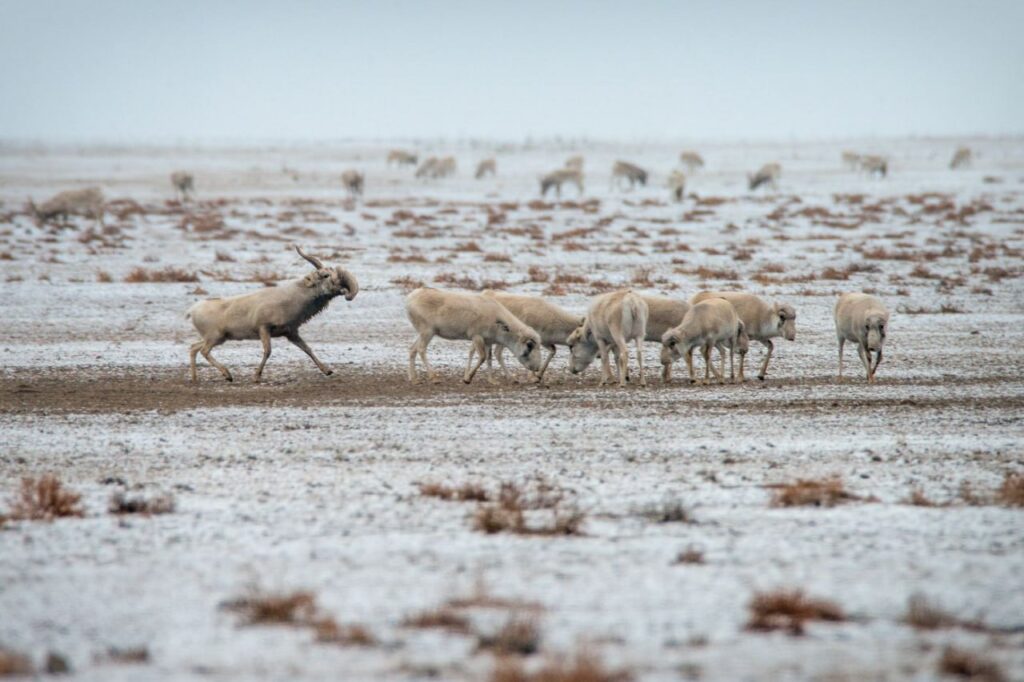
The conservation initiative has overseen a surge in the number of saiga antelope to more than 1.9 million, a 10-fold increase since a devastating disease outbreak in 2015.
“Unlike the Saiga, the Przewalski’s horse prefers a much broader selection of grasses, and in turn distributes the seeds of additional plant species across their shared steppe environment, playing a complimentary role. In addition to this, their dung piles provide nutrients to other plants and decomposers, such as insects,” the initiative said.
A key part of the project is raising awareness about the wild horses among local communities. Conservationists are planning work with children and schools, providing educational materials and coloring books that outline the differences between wild and domestic horses.