For the countries of Central Asia, Victory Day holds a deep significance. Although debates over the nature of the May 9 commemorations have intensified in recent years, the importance of the holiday remains unchallenged.
A War That Touched Every Family
Attitudes toward the celebration marking the defeat of Nazi Germany are largely shaped by each nation’s level of participation in the war effort. Kazakhstan mobilized over 1.2 million people, nearly 20% of its pre-war population of 6.5 million. Of these, more than 600,000 perished at the front, with an additional 300,000 dying in the rear due to malnutrition, forced labor, and inadequate medical care.
With a similar sized population, Uzbekistan sent approximately 1.95 million people to the front – or one in every three residents. Around 400,000 Uzbeks did not return home. Over 500 Kazakhstani and more than 300 Uzbekistani soldiers were awarded the title Hero of the Soviet Union.
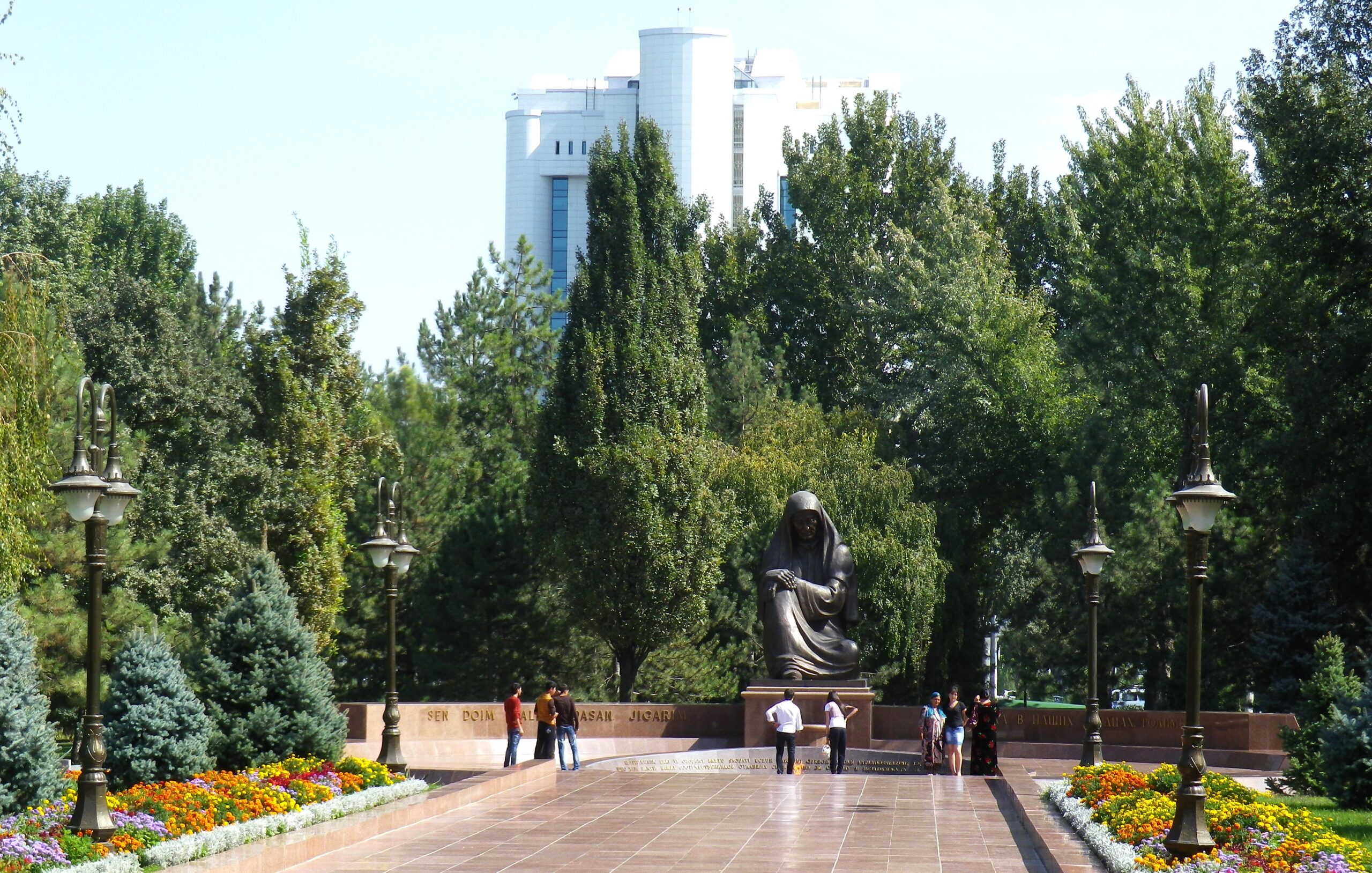

Eternal flame and Crying Mother Monument, Tashkent; image: TCA, Stephen M. Bland
Kyrgyzstan, home to just 1.5 million people at the time, sent over 363,000 to the front. Approximately 100,000 perished, and 73 received the Hero of the Soviet Union medal. Tajikistan mobilized more than 300,000 troops, with over 100,000 never returning. Fifty-five Tajiks received Hero of the Soviet Union honors. Turkmenistan, with a population of 1.3 million, sent around 200,000 soldiers and officers; 16 received Hero status.
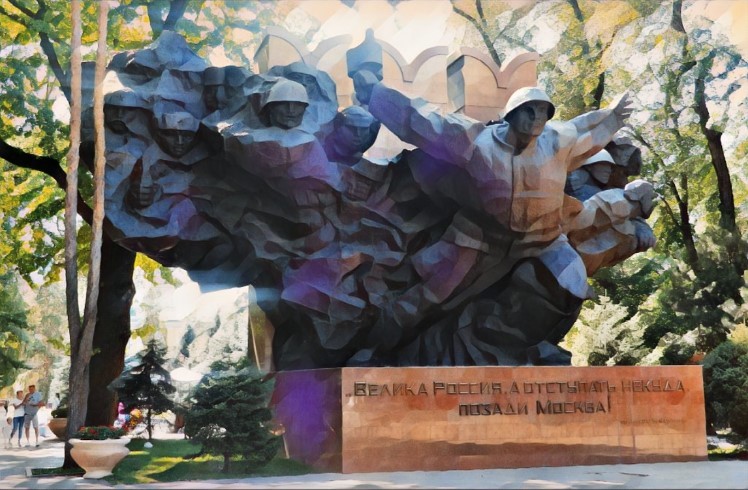
Central Asian soldiers played vital roles in major battles, including the defense of Moscow. They helped liberate territories across the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe. The region also contributed 20-30% of its horse population, then a central component of local economies, for military use.
The war profoundly reshaped Central Asia. Thousands of Soviet enterprises were relocated to the region, fueling industrialization. Millions of refugees from Nazi-occupied zones found sanctuary in Central Asian republics. Many children were taken in by local families and raised as their own.
Today, many in Central Asia feel that outsiders fail to grasp the weight of Victory Day. While countries like the UK, U.S., Italy, and France recorded wartime deaths of 380,000, 417,000, 479,000, and 665,000 respectively, the USSR suffered over 26 million losses. German losses are estimated at 8.4 million.
Celebrating Amid Controversy
Recent years have brought a shift in how Victory Day is perceived in Central Asia. Symbols such as the Guards ribbon, criticized for echoing imperial Russian motifs, have sparked debate. Some argue that the holiday reflects colonial oppression, as the peoples of Soviet Asia were conscripted into a foreign war. These debates have grown louder since Russia annexed Crimea in 2014, with some now viewing the May 9 celebrations as a tool of Russian influence in the region. Nonetheless, Central Asian leaders have rejected efforts to “cancel” Victory Day, reaffirming its deep personal and national resonance.
Efforts to distinguish the celebration from Russian state narratives are evident. Many events now emphasize patriotism rather than Soviet nostalgia. On May 7, Kazakhstan held its first military parade in Astana in seven years, marking both Defender of the Fatherland Day and the 80th anniversary of Victory Day. In Almaty, a procession called Batyrlarğa Tağzym (“Let’s Bow to the Heroes”) will honor Kazakhstani front-line soldiers. This event mirrors Russia’s “Immortal Regiment” but is positioned within a distinct national context.
Veterans will be honored across the region through concerts, shows, community festivals, and financial support. Kazakhstan plans to name over 500 streets after World War II veterans, according to President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev.
Military parades took place on May 8 in Bishkek and Dushanbe. In Tashkent and other Uzbek cities, major festivities are planned. Uzbekistan is leading the region in veteran support, providing $10,000 to each of the 82 surviving war veterans, one of whom is 114 years old. Kazakhstan will grant $9,686.90 to its 111 veterans. Kyrgyzstan’s 32 remaining veterans will receive $1,140 each. In Tajikistan, 17 veterans will receive $4,810, with those in Dushanbe getting an additional $2,000 from the city administration.
In contrast, Russian veterans will receive less than $1,000 each.
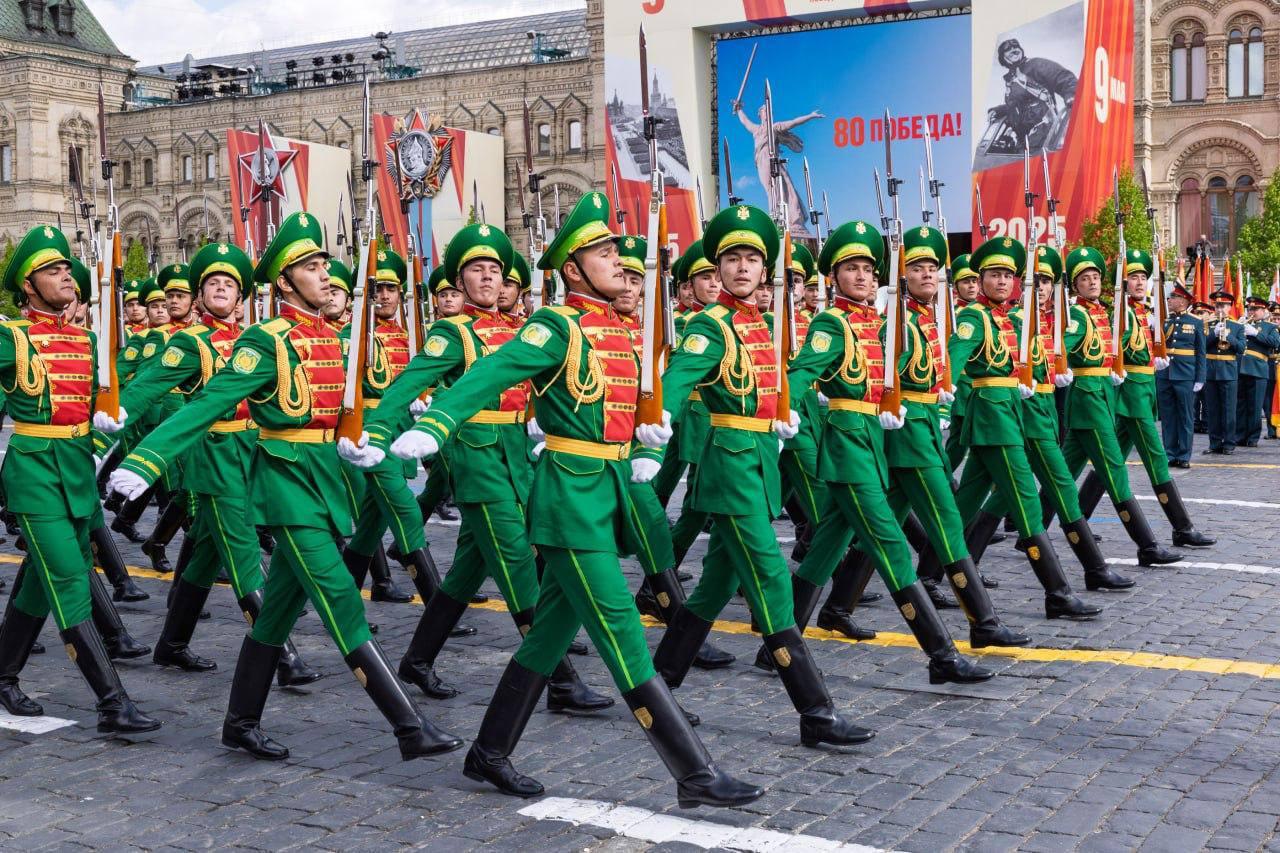

The Turkmen Rifles march in Red Square, Moscow; image: Telegram @ejpredbot
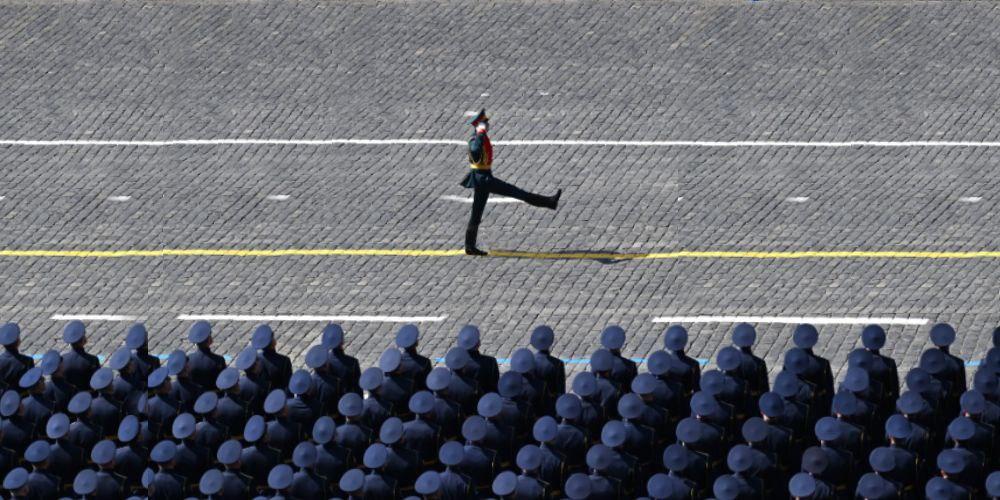
Against the backdrop of ongoing conflicts and shifting alliances, all five Central Asian leaders attended this year’s Victory Day parade on Moscow’s Red Square, which speaks volumes about the region’s delicate relationship with Russia. In Moscow, Vladimir Putin vowed that the Russian army would always stand up to “nazism,” a narrative previously used by Russia to justify its invasion of Ukraine. In one of a number of growing examples of Central Asia’s agency, however, Kazakhstan’s President Tokayev has voiced his support for Ukraine’s territorial integrity